👋 Exciting news! UPI payments are now available in India! Sign up now →
Petty cash book: Format, types, operation, and advantages
All business expenses are equally important and must be tracked to maintain a steady cash flow and not go overboard, which damages the baseline. So, petty expenses are also one of the business spending categories, and this also has to be managed properly.
You might think that petty expenses are of small amounts and can be made on the go; why do you have to account for those as well? This is because these expenses can add up and become huge and managing it afterward can be extremely tricky.
Learn about petty expenses, what is a petty cash book, petty cash book format, types of petty cash books, and much more.
What is a petty cash book?
First, let’s start with what is petty cash. It is a small amount of company funds kept aside to make minor or not-so-significant purchases. For example, daily travel tickets, office tea or coffee, sanitary products for the workspace, stationary, etc.
Now a petty cash book is a record account or cash account to take care of any expenses falling under the petty cash category. This means that instead of making these purchases with cheques or cards, you use tangible cash and coins.
You need to maintain a separate petty cash book from the actual accounting books because if all these small transactions are counted in the main cash book, your overall record will be overburdened.
A petty cash book is just a way to isolate these insignificant expenses from the major business transactions.
How does a petty cash book work?
A petty cash book is not similar to your computer accounting record. Instead, it is a ledger book used to note down all petty expenses.
Whenever there is any payment made for smaller office or business expenses, that expense is recorded along with the amount and date in a petty cash book. Every company has a petty cashier who is responsible for maintaining the petty cash book.
Basically, the petty cashier receives money from the head accountant in the form of a cheque. That cheque is then converted to cash in the bank and recorded on the receipts side of the petty cash book.
Whenever an expense requirement is raised, the petty cashiers make a Petty Cash Voucher (PCV). Before giving this PCV, the cashier records the particulars of the expense, amount, date, and petty cash voucher number.
PCV has to be approved by the responsible authority before the payment is made.
Steps to record petty cash transactions in a petty cash book
Efficiently recording petty cash transactions is integral to maintaining financial transparency. This section outlines a systematic approach to documenting these transactions in a petty cash book, ensuring accuracy and facilitating streamlined financial management.
1. Opening balance
Initiate the petty cash record with an accurate opening balance. This balance represents the amount of cash available in the petty cash fund at the beginning of the accounting period. Ensure that the opening balance of the petty cash fund is accurately recorded. The opening balance will change every financial period depending on the leftover balance from the previous period.
2. Record cash expenses as per category
Categorize and record cash expenditures meticulously. Categories that are generally assigned by businesses include food & meal costs, hotel & lodging costs, travel & commute costs, sales & marketing costs, and so on.
It is important for a business to define these categories clearly so that it helps you analyze where most of your petty cash funds are being used. Assign each transaction to specific categories to provide a clear breakdown of how petty cash is utilized, enhancing expense tracking and financial analysis.
3. Petty cash vouchers
Support each transaction with a petty cash voucher. A petty cash voucher is nothing but a simple way of detailing the different aspects related to any petty cash expense. These vouchers should detail the purpose, amount, and date of the expenditure, creating a comprehensive trail for auditing and ensuring transparency in fund utilization.
4. Closing balance
Maintain an up-to-date closing balance after each transaction. This running balance reflects the remaining funds in the petty cash, aiding in real-time monitoring and facilitating quick assessments of available resources.
Being able to see the closing balance helps people decide how much they should spend and where is it that they should invest the remaining funds. Without the visibility of available funds, employees may end up making decisions that are not financially sound.
5. Record fund replenishment
When the petty cash balance approaches depletion, record the replenishment of the fund. Document the inflow of funds, whether it's through cash injection or reimbursement, to maintain the operational continuity of the petty cash system.
Doing this is very important from a finance team point of view as it ensures that employees who really need the funds are not left having to use personal funds for business purposes and then wait for weeks and months to receive their reimbursement.
Simplify petty cash management to streamline your processes
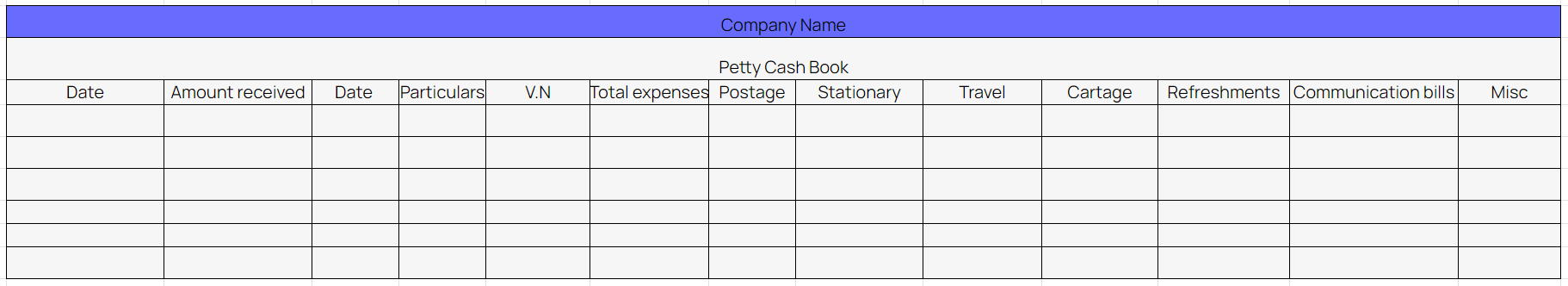
Petty cash book format
This is what a general petty cash book looks like
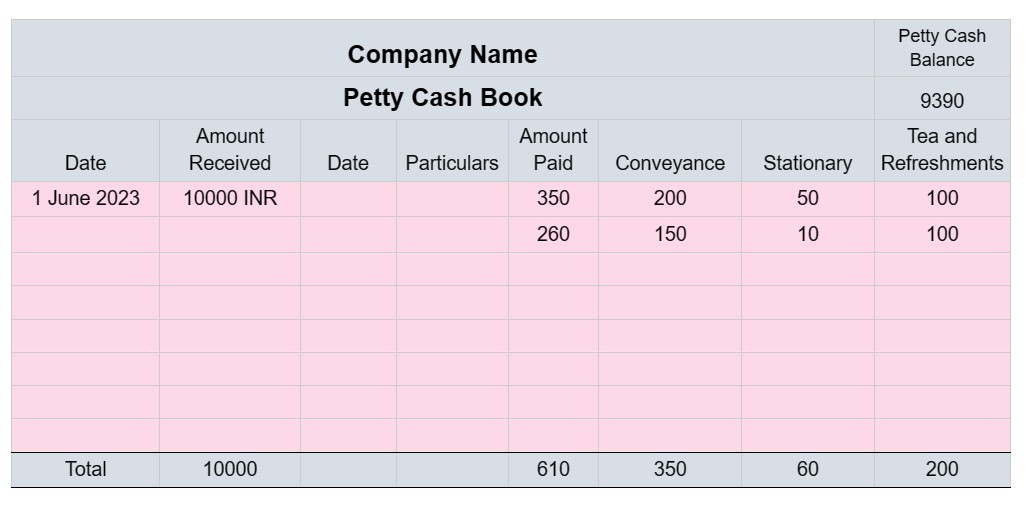
As shown in the image, all expense categories have a specific column. Individual expense amounts are recorded to get the total spending from the given money and the total spending of particular categories.
What are the different types of petty cash books?
There are two standard types of petty cash books:
1. Columnar petty cash book
A columnar petty cash book has two sides — one for the debit entries and one for the credit entries. This cash book style includes various columns to monitor everyday transactions.
There are separate columns to track each transaction's specifics, date, and debit or credit amount. The credit side has columns for all the cash expenses set in chronological order.
The money that comes from the head accountant is recorded on the debit side. Every time an expense is made, it is recorded under its specific column. Everything is tracked in a sequence.
In the end, there is a total money column on the credit side that tells you how much the total expense was.
Format of columnar petty cash book
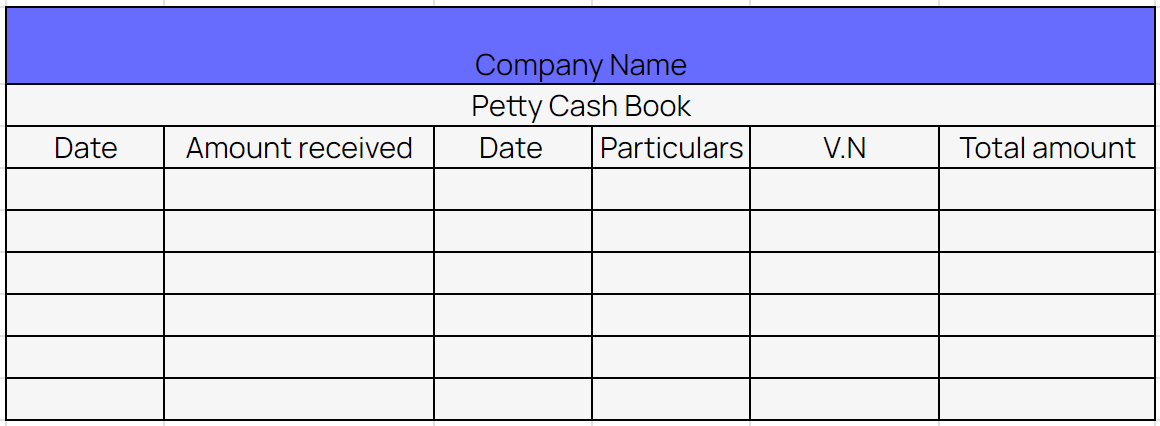
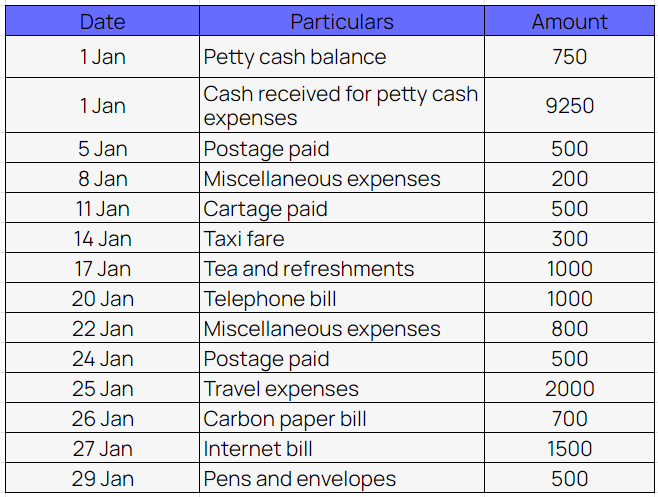
Example of columnar petty cash book
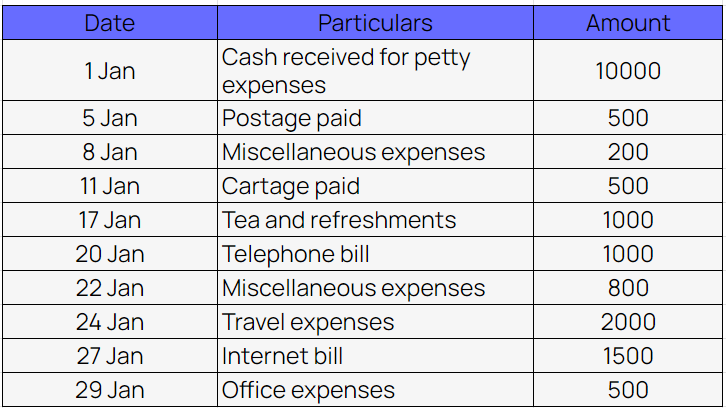
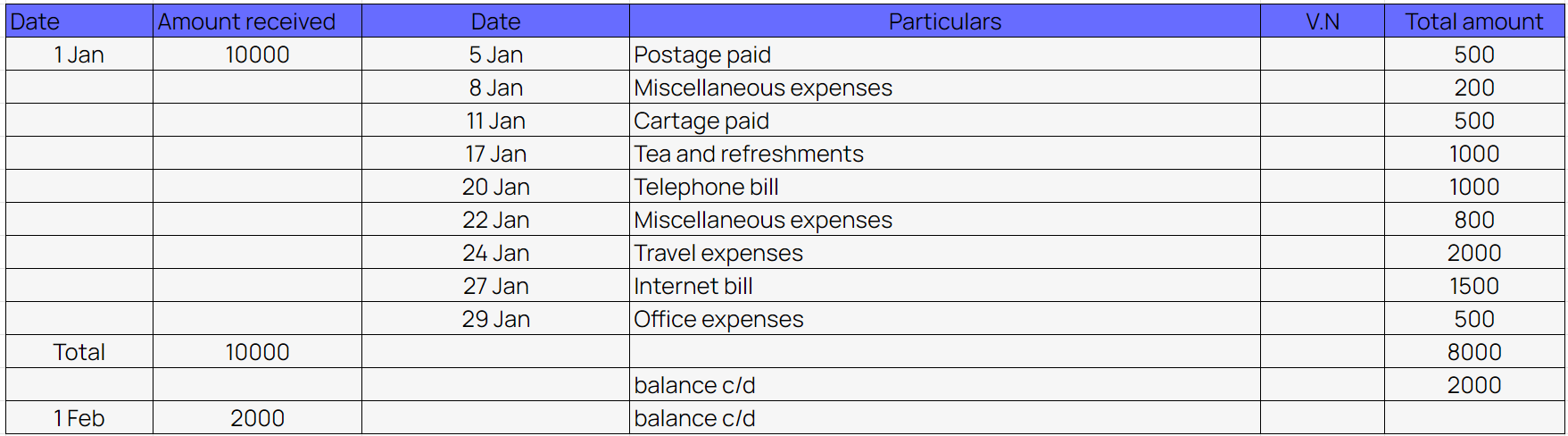
2. Analytical petty cash book
An analytical petty cash book is different from the previous one as it has on single cash field on the debit side and a separate date field. The rest is as the columnar petty cash book.
The funds that the head accountant gives are stored before the expenses actually happen. Each petty cash expense has a separate column, and the totals of each expense are calculated automatically.
The amount in the total column is the same as that in the specific expense column.
Format of analytical petty cash book
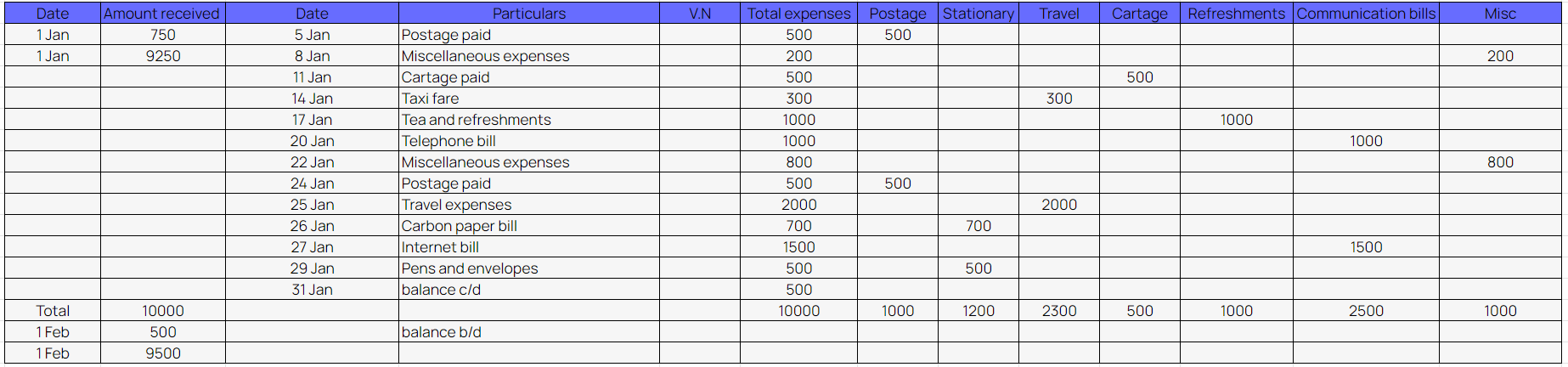
Example of analytical petty cash book
What are the different systems for maintaining petty cash book?
There are three petty cash book maintenance systems:
1. Open system of petty cash
The open system of petty cash maintenance is simple. The petty cashier is given a ballpark figure of money to handle the petty cash expenses. Once that amount is exhausted, the petty chairs submit the expense record to the head accountant.
After this, an approximate figure is given again, and the cycle repeats.
2. Fixed system of petty cash
Unlike the open system, here, the petty cashier is given a fixed amount of money for a fixed amount of period. Once the period is over, the cashier submits the petty cash book account to the head accountant.
After this, that fixed amount is refunded, and the cycle continues. This is a great way to keep your petty expenses under a budget. Having a fixed amount limits anything extra to be purchased or paid for.
3. Imprest system of petty cash
In contrast to the previous method, the petty cash maintenance imprest system is extremely popular. In this method, a total amount for petty cash expenses is calculated for a period of time, and that amount is advanced as the budget for that duration.
This amount is given as petty expense budget is called imprest cash. Once the duration is over, a detailed report is submitted to the head accountant, which means that the petty cash account is now back to zero.
Again the same process is repeated of calculation and advancing budget amount.
Track, control, and monitor your petty cash expenses effortlessly
What are the steps in setting up a petty cash system?
Setting up a robust petty cash system is foundational to effective financial management. This segment outlines the systematic steps involved in establishing a petty cash system, ensuring transparency, security, and efficiency in handling minor expenditures within an organization.
1. Establish petty cash policies and procedures
The first step when creating a petty cash system is to establish a list of rules and regulations that will make up the policy governing the usage of the petty cash fund. Define clear policies that outline how petty cash can be used, including approved expenses, spending limits, and documentation requirements.
Develop procedures for obtaining approvals, recording transactions, and periodic audits to ensure compliance.
2. Employ a petty cash custodian
Select a reliable and trustworthy individual as the petty cash custodian. This person should be responsible for safeguarding the funds, maintaining accurate records, and ensuring adherence to established policies and procedures.
A company can assign anyone within the organization to carry this responsibility. Usually, it is someone from the finance team or the administrative team who is given the role of a custodian.
3. Determine the amount of petty cash you need
Conduct a thorough assessment of the organization's day-to-day operational needs. Consider the frequency and nature of minor expenses to determine an appropriate amount for the petty cash fund, striking a balance between accessibility and security.
The petty cash fund should have enough money to cover the daily expenses of employees who have access to it. But at the same time, you also want to ensure that excess cash isn’t left in this fund as there is always the risk of theft or fraud.
4. Finance the petty cash account
If the petty cash is being withdrawn from an account that is already used for other purposes, it can be confusing to segregate expenses as it will be hard to track whether a certain transaction is petty cash related or for some other reason.
Allocate the determined amount to a dedicated petty cash account. This segregation ensures financial clarity and simplifies monitoring. The account should be easily accessible to the petty cash custodian while maintaining security protocols.
5. Ensure the security of the petty cash funds
Implement stringent security measures to protect petty cash funds. This includes secure storage, restricted access, and transport protocols. Clearly communicate security procedures to the petty cash custodian and relevant staff members.
For modern petty cash systems that are digital, you must ensure that there are sufficient IT measures in place to avoid any kind of theft through hacking.
6. Ensure bookkeeping and monitor every spending
Establish a detailed bookkeeping system to record each petty cash transaction. Doing so can also later help in transferring all the details to your accounting system. The system should capture essential details such as date, purpose, amount, and receipts.
Missing data can be a pain for the finance team as they won’t be able to log those entries in the accounting system. Regular monitoring by the petty cash custodian ensures accuracy and transparency in financial records.
7. Request for receipts
Enforce a policy requiring employees to provide receipts for every petty cash transaction. Many expense management systems nowadays have mobile apps that let employees submit pictures of the receipts.
This helps the employees as they don’t have to keep collecting paper receipts till the end of the month for lengthy expense reports. Receipts serve as tangible evidence of expenditures, aiding in documentation, and ensuring that each transaction aligns with the organization's policies.
8. Ensure timely replenishment of funds
Institute a clear process for the timely replenishment of petty cash funds. Regularly assess the balance and initiate replenishment to prevent shortages that may disrupt operational activities.
The custodian when doing their regular checks of the petty cash funds will get a good idea of when it needs replenishment. This proactive approach maintains the fund's functionality.
9. Provide training to employees
Even though you draft and share the policies with employees, they may forget certain rules or not pay close attention to the details. This is why you must conduct training sessions to educate employees on petty cash policies and procedures.
Ensure that staff members understand the proper utilization of petty cash, emphasizing the importance of adhering to established guidelines for accountability and compliance.
10. Ensure periodic petty cash audits
Schedule regular audits of the petty cash system to verify the accuracy of records. Audits serve as a critical mechanism for detecting discrepancies, ensuring adherence to policies, and maintaining the integrity of financial records.
The custodian can be responsible for conducting these audits, but you can also set someone else from the finance team to do this. This helps to ensure that there are double layers of security and checking the fund apart from just the custodian.
11. Adapt to changes with regular revisions
Acknowledge the dynamic nature of organizational needs and financial environments. Regularly review and revise petty cash policies and procedures to accommodate changes, whether in spending patterns, industry regulations, or internal structures.
After a few months or after conducting audits, you may notice patterns and gain insights regarding the petty cash fund which tells you to change the way certain things are done in order to make the process easier or more efficient for the company and its employees.
12. Consider integration with a petty cash management system
Explore the integration of modern technology through a petty cash management system. Automated systems can streamline processes, providing real-time insights into fund utilization, reducing administrative burdens, and enhancing overall efficiency in petty cash management.
What are the advantages of imprest petty cash book?
The imprest petty cash book stands as a beacon of efficiency in financial management. This segment touches upon the notable advantages of adopting the imprest system for petty cash, showcasing its impact on simplicity, control, transparency, and overall operational effectiveness.
Simplified and easy-to-use system
The imprest system streamlines petty cash management, offering a straightforward and user-friendly approach that minimizes complexities and fosters ease of use for employees and financial personnel.
Increased control and accountability
By necessitating periodic fund replenishment, the imprest system enhances control and accountability. The predetermined fixed amount ensures that petty cash remains a manageable and monitored resource.
Improved cash flow management
The imprest system facilitates improved cash flow management. Regular replenishments and a clear understanding of petty cash usage contribute to a more precise assessment of cash inflows and outflows.
Ensures transparency
Transparency is a hallmark of the imprest system. Clear documentation and a fixed fund amount provide transparency into how petty cash is utilized, aiding in internal oversight and external audits.
Periodic fund replenishment
The imprest system's requirement for periodic fund replenishment ensures that the petty cash remains adequately funded, preventing shortages and disruptions in operational activities.
Reduces operational burden
Implementing the imprest system reduces the operational burden associated with petty cash management. With a predetermined fixed amount, the need for constant monitoring and adjustment is minimized.
Reduced risks of fraudulent expenses
The imprest system's structured nature acts as a deterrent to fraudulent activities. With clear guidelines and periodic reviews, the risks of unauthorized or fraudulent expenses are significantly reduced.
Minimizes labour efforts
The streamlined processes of the imprest system minimize the labor efforts required for petty cash management. This allows personnel to focus on more strategic financial tasks, improving overall operational efficiency.
Facilitates verification and auditing process
Verification and auditing become more straightforward with the imprest system. The fixed amount and clear documentation ease the process of validating petty cash transactions during internal audits or external scrutiny.
Ensures scalability
The imprest system is adaptable to varying business sizes. Its scalability makes it suitable for both small enterprises and larger corporations, providing a flexible solution that can grow with the organization's needs.
Take control of your petty cash with our expense management solution
How is petty cash operated - Step by step guide
All company expenses, in general, are made through cheques or online fund transfers. However, when it comes to petty expenses, instead of cheques, cash is used. Here is how petty cash is operated:
Step 1: Funds creation
Your first step is to select and appoint a petty cashier. This cashier is responsible for all activities related to petty cash funds and expenses. A certain amount of funds is given to this employee in the form of a cheque.
This cheque is then converted to cash and stored to make payments. As the petty cash fund is a fixed amount, there is no need for a new journal entry every time the funds are refreshed.
Step 2: Making payments
Now that the petty cashier has the funds, day-to-day business expenses can be made easily. Plus, all these will be made in compliance with the company expense policies.
So, if the business finance heads have put restrictions on some category of expenses or specified a particular vendor for specific expenses, all those rules will be duly followed.
All the expense receipts of petty cash vouchers have to be signed by the cashier and the one receiving them. Petty cash funds decrease with every expense. This means that the total spend must be equal to the total amount allotted in the beginning.
Only then will the petty cash book be approved by any auditor.
Step 3: Refunding
Once the previously allotted amount is exhausted, the petty cashier has to submit a request for a refund.
For this, they are required to submit a petty cash expenditure statement and a collection of all the receipts to the finance department of the company. All of the data is verified, and only then another cheque for the next time period is issued.
How to post petty cash to the ledger?
Here is an example of how petty cash is posted in a ledger
- [ "Wages" ]
- [ "Stationary" ]
- [ "Tea and refreshments" ]
- [ "Internet" ]
- [ "Conveyance" ]
- [ "Total" ]
The head accountant gives the petty cashier a cheque for 103000 INR; it is recorded in the primary cash book. The credit side will show a total of 103000 INR to denote total payments.
Then all the above categories of payments are deducted from the journal. So wages, stationary, followed by tea and refreshments and so on. Now the total amount given will equal the total amount spent.
What are the advantages of a petty cash book?
In business finance, the petty cash book stands as a crucial tool for effective expense management. To understand what is a petty cash book and the petty cash book format, you must explore the different formats, types, operations, and most importantly, the myriad of advantages that maintaining a petty cash book can help you get for your business.
Simplifies expense management
The pivotal advantage lies in the simplification of expense management. By allocating a distinct fund for minor outlays, the petty cash book establishes a structured framework, facilitating a more organized approach to expense tracking and categorization.
Having a specific book, journal, or digital record system as a petty cash book where all the small expenses of the business are noted is extremely important for accounting purposes later on.
Monitors small expenditure
While small expenses may not be considered very important to take note of, they can add up over time and have a significant impact on the finances of the company.
Recognizing the cumulative impact of minor expenses, the petty cash book serves as a meticulous monitor, capturing and documenting these seemingly inconspicuous transactions. This vigilance contributes to a more accurate representation of the overall financial landscape.
Ease of reconciliation
In accounting, reconciliation is the process of ensuring that two sets of records are in agreement. Further, account reconciliation involves resolving any discrepancies that may have been discovered. A noteworthy benefit of maintaining petty cash books is the streamlined reconciliation process.
With a dedicated record of petty cash transactions, businesses can effortlessly reconcile their accounts. This helps in minimizing discrepancies and enhancing the accuracy of financial reports during audits or assessments.
Reduces the burden of paperwork
Traditionally, petty cash books were physical paper books where the transactions had to be manually noted. While they offer the same benefits as modern digital petty cash books, they are more prone to damage and loss of data.
In a digital era that grapples with an overload of paperwork, the introduction of a digital petty cash book offers respite. It trims down the administrative burden associated with minor expenses, fostering a more sustainable and eco-friendly financial ecosystem.
Reduces fraud risks
Establishing a culture of accountability is pivotal in reducing fraud risks. The digital petty cash book, by maintaining a transparent record of small-scale transactions, acts as a deterrent to potential fraudulent activities, reinforcing the financial integrity of the organization.
Many of these modern petty cash book systems have automation that allows them to retrieve transaction data in real-time through payment methods that are linked to the system.
Ensures quicker reimbursement
Employee satisfaction and operational efficiency intertwine in the realm of petty cash management. When the petty cash book is constantly updated and maintained properly on a regular basis, then the reimbursement of employee expenses can also happen faster.
The petty cash book expedites the reimbursement process, ensuring that employees are promptly compensated for their out-of-pocket expenditures, thereby fostering a positive and responsive organizational culture.
Facilitates expense analysis
For businesses committed to strategic financial planning, a granular analysis of expenses is indispensable. The petty cash book, with its detailed records, serves as a valuable tool for dissecting small-scale transactions.
These transactions are then analyzed by the analytics tools present within the system that provide insights and contribute to informed decision-making for the future financial planning of the business.
Simplify petty cash management to streamline your processes
What is the importance of regular reconciliation of petty cash books?
Regular reconciliation of petty cash books is a pivotal practice in financial management. This segment underscores the significance of this process in maintaining accuracy, accountability, and financial transparency within an organization.
Ensures identification of discrepancies
Regular reconciliation acts as a meticulous detective, unveiling any discrepancies that may arise between the recorded transactions in the petty cash book and the actual expenditures incurred. This early identification is pivotal in maintaining the integrity of financial records.
The reconciliation process also helps to ensure that when audits are conducted by external auditors, they find the least amount of errors if any at all. This helps in maintaining the integrity of the organization.
Ensures prompt resolution of discrepancies
Identifying discrepancies is only the first step; the subsequent prompt resolution is equally crucial.
When reconciliations are conducted at shorter and more regular intervals rather than waiting for the end of a financial period, it helps to avoid many financial pitfalls and stay away from major issues that might have otherwise gone unnoticed and caused major damage to the company.
Regular reconciliation ensures that any discrepancies are addressed promptly, preventing the accumulation of errors that could lead to larger financial inaccuracies.
Ensures timely replenishment of funds
Understanding the actual utilization of petty cash is vital for maintaining operational fluidity. Regular reconciliation reveals the true extent of cash usage, facilitating timely fund replenishment and preventing potential disruptions due to shortages.
After a few reconciliation cycles, the finance controller or finance team member responsible for conducting the reconciliations gets a good idea of when they should replenish the funds so that the employees don’t face a situation where their operations come to a halt due to a lack of funds.
Prevents fraud
Beyond its role in accuracy, reconciliation serves as a robust defense against fraudulent activities. Whether it is intentional or unintentional, fraud can take place if the transactions being recorded are not checked thoroughly.
By scrutinizing transactions regularly, irregularities that might indicate unauthorized or fraudulent expenses can be detected early, mitigating the risks associated with financial malfeasance.
Assures policy compliance
Financial policies and procedures form the backbone of responsible financial management. Regular reconciliation serves as a litmus test, ensuring that every petty cash transaction aligns with established guidelines, thereby fostering a culture of policy compliance within the organization.
Without proper and periodic reconciliation of the petty cash book, non-compliant errors may go unnoticed and hinder the authenticity of the financial statements of the company.
Assists in recognizing spending patterns
Regular reconciliation transforms data into insights, offering a nuanced understanding of spending patterns. This knowledge becomes a strategic asset, allowing organizations to make informed decisions and adjust budgets based on observed trends in petty cash expenditures.
Whether the reconciliation is being done manually by a finance team member or through the help of automation software, both methods help you spot patterns and understand the utilization of funds in a better way.
Financial transparency
Transparency is not just an ethical principle but a fundamental requirement in financial management. Regular reconciliation aligns recorded transactions with actual expenditures, providing a clear, unobstructed view of the organization's financial health to internal stakeholders, auditors, and external entities.
When there is a lack of transparency regarding the financial situation of the company, it can lead to a lack of trust in the organization and external stakeholders.
Enhances accountability
Regular reconciliation is an accountability mechanism. The reconciliation process enforces accountability on employees to use their petty cash funds judiciously and in line with the company’s policies because they know that if something is wrong, it will be spotted during the reconciliation process.
It places a responsibility on individuals to ensure the accuracy of petty cash records, fostering a culture where financial responsibility is ingrained at every level of the organization.
What are the challenges with maintaining a petty cash book?
While a petty cash book offers a myriad of advantages, its implementation is not without challenges. This section delves into the hurdles associated with maintaining a petty cash book, shedding light on potential pitfalls that businesses need to navigate for effective financial management.
1. Risk of misuse
Employees may often use the petty cash fund for a particular reason that might not be permitted as per the business policy and report it to be some other type of expense instead. The inherent cash nature of petty cash creates a vulnerability to misuse.
There's a potential risk of funds being used for unauthorized or personal expenses. This makes it very important to put stringent measures in place so as to prevent financial impropriety.
2. Lengthy bookkeeping
The meticulous recording of numerous small transactions can make bookkeeping a time-consuming endeavor. The sheer volume of entries poses a challenge, demanding dedicated effort and attention to detail in the bookkeeping process.
This may often require a company to hire an accountant capable of managing these accounts. Doing this might not be a problem for some businesses but may be seen as an additional expense for the company.
3. Chances of non-compliance errors
Maintaining compliance with financial regulations, whether it is internal or external, is of utmost importance. The manual nature of petty cash bookkeeping increases the likelihood of inadvertent errors, making businesses susceptible to compliance issues that may arise during audits.
Even simple errors can cause a huge loss in finances. Furthermore, it takes days and weeks sometimes to rectify the errors. This causes a lot of damage to the overall efficiency of the business.
4. Possibility of theft
The physical presence of cash, even in modest amounts, introduces the risk of theft. Businesses need to implement robust security measures to safeguard the petty cash fund and mitigate the potential loss through pilferage.
For small businesses, this is often an added burden. And theft is just one of the many risks associated with losing your petty cash funds. Other risks include loss due to natural disasters or internal fraud.
5. Lack of detailed documentation
While petty cash records capture transactions, they may lack the depth of documentation required for a comprehensive financial overview.
This is usually the case when petty cash books are maintained for the sake of being maintained rather than formatting and including data about each transaction that is actually useful and may help gain important insights at the end of a financial period.
Insufficient details can pose challenges during financial analysis, hindering the extraction of meaningful insights.
6. Not suitable for large businesses
Petty cash systems are designed for managing minor expenditures, making them less suitable for large businesses with extensive and diverse financial transactions. Scaling up can result in a loss of efficiency and control over the cash management process.
7. Requires periodic reviews
Neglecting regular reviews of the petty cash book can lead to discrepancies and oversight. There might be errors in data entry or compliance issues that are causing trouble in the finances of the company.
Businesses need to establish a routine for periodic reviews to ensure accuracy, identify anomalies, and address any emerging issues in a timely manner. Ideally, a financial controller or a member of the finance team should be responsible for checking, reviewing, and auditing the petty cash book at a fixed interval.
Simplify tracking, reduce errors, and enhance transparency
What is the role of technology in petty cash management?
Technology stands as a catalyst in reshaping the traditional contours of petty cash management. Automation technology has brought efficiency and transparency to the traditional petty cash management process. This transformative role is particularly evident in the implementation of advanced technologies that redefine how organizations handle minor expenditures.
Disburse petty cash funds digitally
Move beyond physical cash handling by adopting digital disbursement methods. Giving employees personal corporate prepaid cards is a great alternative to handing out physical cash. It is much easier to handle and also has many benefits as compared to physical cash.
This entails directly transferring petty cash funds digitally, eliminating the need for manual cash transactions. This not only enhances convenience but also reduces the inherent risks associated with physical cash handling.
Leverage petty cash management software
Integrating dedicated petty cash management software provides a centralized platform for overseeing petty cash transactions. These software solutions automate record-keeping, transaction tracking, and reporting. It eliminates the manual and repetitive tasks involved in managing the petty cash of a company such as data entry.
Leveraging a software solution also helps ensure that all transactions are centralized in one place. All these features and benefits improve accuracy, efficiency, and real-time insights into the status of petty cash funds.
Assign prepaid cards to employees
Optimize expense control by assigning prepaid cards to employees. For instance, Volopay corporate cards offer a tailored solution for managing petty cash digitally.
They provide a secure and controlled spending mechanism, detailed transaction tracking, and enhanced security, minimizing the risks associated with traditional cash or reimbursement methods.
You get security features like temporary card freezing and permanent blocking through the mobile app or the web platform. This helps safeguard the money in your card from being used by anyone else even if the card is lost or stolen.
Implement digital petty cash vouchers
Replace traditional manual voucher systems with digital alternatives. Digital petty cash vouchers streamline the authorization and documentation process for minor expenses.
This not only reduces paperwork but also ensures a secure and traceable method for recording and validating expenditures.
Since it is digital in nature, managers and admins of an employee are also notified of petty cash withdrawals helping everyone stay on top of expenses.
Integration with accounting software
Ensure seamless integration with accounting software. Most expense management software available in the market that will act as your petty cash management system have the ability to integrate with many of the accounting tools.
This connectivity automates the transfer of petty cash transactions into the general ledger, reducing manual data entry, minimizing errors, and providing a comprehensive and up-to-date view of financial records.
Monitor expenses in real time
Harness technology to enable real-time monitoring of petty cash expenses. Rather than waiting for employees to report their expenses every day or every week, expense management software automatically tracks the transactions they have made using linked payment methods provided to them such as prepaid cards.
Automated systems provide continuous tracking of expenditures, offering immediate awareness of how funds are utilized. This real-time monitoring enhances control and facilitates timely decision-making based on current financial data.
Utilize expense reports and analytics
Generate detailed expense reports and leverage analytics tools to extract valuable insights from petty cash data. Finance teams in companies could of course do this without software systems, but it would take a lot of manual effort and time to do so.
These digital analytics offer a nuanced understanding of spending patterns, enabling informed decision-making and strategic adjustments to optimize petty cash allocations.
Incorporate security measures
Implement advanced security measures to safeguard digital petty cash transactions. This includes robust encryption protocols, secure access controls, and multi-factor authentication, fortifying the system against potential fraudulent activities and unauthorized access.
Even the payment methods linked to the petty cash management system are equipped with robust security measures.
Automate reconciliation and reimbursements
Automation extends to the reconciliation process, ensuring accuracy in financial records. For example, when employees submit receipts for their expenses, the system not only stores them for reference purposes but can also scan the document to identify whether it matches the details of the transaction that it is associated with.
Automated systems facilitate the reconciliation of petty cash transactions, reducing manual effort and minimizing the chances of discrepancies. Additionally, the reimbursement workflow can be automated, streamlining the approval and reimbursement cycle, thus ensuring a smooth flow of funds back into the petty cash system.
Technologies that can be integrated into the petty cash system
In the ever-evolving landscape of financial management, the integration of cutting-edge technologies into petty cash systems has become instrumental. This segment explores several innovative technologies that organizations can seamlessly incorporate, augmenting the efficiency, security, and oversight of petty cash transactions.
1. Expense management software
Embrace the power of expense management software to revolutionize petty cash tracking and reporting. These sophisticated platforms offer a centralized hub for managing petty cash transactions.
Using such a system, all your petty cash transactions will be automatically tracked in real-time under a single dashboard. Features include automated record-keeping, receipt scanning through mobile apps, and the ability to generate custom reports based on different parameters. This provides unparalleled accuracy and efficiency in financial management.
2. Prepaid cards
Modernize the petty cash system by integrating prepaid cards. These cards offer a secure and convenient alternative to handling physical cash that is more prone to loss or theft.
A prepaid card is much more secure in terms of the safety of your funds as you can block it through a digital system once you realize that it has been stolen or lost.
With controlled spending limits and detailed transaction records, prepaid cards enhance transparency, reduce the risk of misuse, and simplify the overall tracking of petty cash expenditures.
3. Reimbursement workflow automation
Being able to automate certain parts of the reimbursement process within your company is also another feature that comes under expense management software. Streamline the reimbursement process through workflow automation tools.
These systems automate the approval and reimbursement cycle, minimizing manual intervention. By digitizing and standardizing the reimbursement workflow, organizations can reduce processing times, enhance accuracy, and ensure a seamless flow of funds back into the petty cash system.
4. Mobile applications for notifications and alerts
It isn’t farfetched to say that everyone involved in business across the world has a smartphone device. These devices are much more handy and quicker to access than work desktops and laptops.
Companies should harness the power of mobile app versions of their petty cash systems to bolster communication and oversight.
Mobile apps can deliver real-time notifications and alerts to designated personnel. Whether it's transaction approvals, fund replenishment needs, or discrepancies, these mobile alerts ensure immediate awareness, enabling swift and informed decision-making.
Best practices for petty cash management
1. Set clear spending guidelines and limits
This is a common but important one. Setting spending guidelines and limits. To ensure fraud aversion and avoid overspending, putting a ceiling limit on each petty expense category or type is essential.
So, for example, the petty expenses categories of your business are refreshments, bus tickets, office stationery, postage, and other miscellaneous expenses.
Now according to the previous spend analysis time frame, you can evaluate and decide on a fixed spend amount for each type. Plus, you also have to list down rules for making these expenses, like process, receipt requirements, voucher validity, etc.
2. Implement regular audits and surprise checks
Maintaining a petty cash book using any of the above-mentioned systems has one crucial step — regular auditing and rechecking. The petty cashier has to submit the expense record at regular intervals.
These regular audits will help to avoid any errors or loopholes in the system. Along with the regular ones, the head accountant or financial manager must sometimes call for surprise checks as well.
These surprise checks are important to check if any employee is getting away with fraud and that everything is maintained according to the process.
3. Maintain proper documentation and receipts
This can be tedious but is extremely essential. Ask your employees and the petty cashier to keep a record and store all the expense receipts. Having paper documents and receipts for petty expenses might sound negligible; however, with these, you can always tally up the amount that was allotted and the expenses that were made.
You can be sure that no amount digits were altered in the book and that all expenses were compliant with the spending policies.
4. Make centralized controls
Even though the petty cash book is maintained by a petty cashier, the head accountant must look over it. Plus, all the expense policies for other businesses and petty expenses should follow the same baseline.
This helps to maintain centralized control. The business will always have streamlined expense management and error-free audits if everything is divided from the top down with the same policies company-wide.
Manage your business petty cash easily with Volopay!
All business expenses have to be managed and tracked properly. Everything boils down to what type of tool and systems you use for this. Let us introduce you to the ultimate tool for expense management — Volopay!
An all-in-one spend management platform designed to make financial management a piece of cake for all businesses.
When it comes to petty cash management, one of the tools offered by Volopay is the best solution for it. Prepaid cards can be assigned to your employees with individual card spending limits. Any expense under the allocated funds will be automatically approved. Anything over that will require approval.
All the expenses are tracked in real-time and recorded in a centric database. This database can be accessed anytime. Moreover, these prepaid cards ensure that all transactions are in compliance with company policies. Anything suspicious will be automatically flagged.
Now let’s come to the tedious problem of maintaining a petty cash book. Volopay prepaid cards and expense management system take care of that as well. With a direct accounting integration feature, all expenses are automatically entered into the accounting sheets.
All the data is accurate with the help of auto-categorization and expense mapping rules.
FAQ's
A petty cash book is an account or record of all petty cash expenses of your business.
All daily expenses and some other insignificant expenses are counted under the petty cash book. For example, team, bus tickets, postage costs, stationary, etc.
Petty cash is recorded as a debit on the company’s asset reports.
Single column, two columns, and three columns.
A petty cashier prepared a petty cash book.
Volopay offers unique prepaid corporate cards that help you track all expenses in real-time, set spending limits, and ensure compliance without much effort. Everything is automated once set up.
There are three petty cash maintenance systems — Open system, Fixed system, and Imprest system.
Petty cash funds are used to make petty expenses. This is a certain amount allotted by the company for making petty expenses for a specific period of time.