Guide on international money transfers for business
If you have dealt with international wire transfers, you’d probably fill that blank with the word ‘expensive’. And you know exactly why. As a small business, every penny that you spend is important. And foreign money transfers can cost you a hefty fee.
The traditional way of sending money internationally involves banks who charge a markup fee depending on the amount of money you are sending and the currencies involved.
Over the years though, many new ways of wiring money across borders have emerged that are much cheaper and can save you a lot of money over time.
What is an international money transfer?
Simply put, an international wire transfer refers to money that is being sent between two countries from one individual or a business to another using an electronic method. Since 92% of the world’s money exists in the form of digital data, it is not physical money that is sent, but rather a piece of information that is exchanged.
The transaction can take place through banks, specific providers like Western Union/MoneyGram, or other third-party money transfer service providers. Businesses send money internationally through online wire transfers as they’re known to be fast, safe, convenient, and have a global reach.
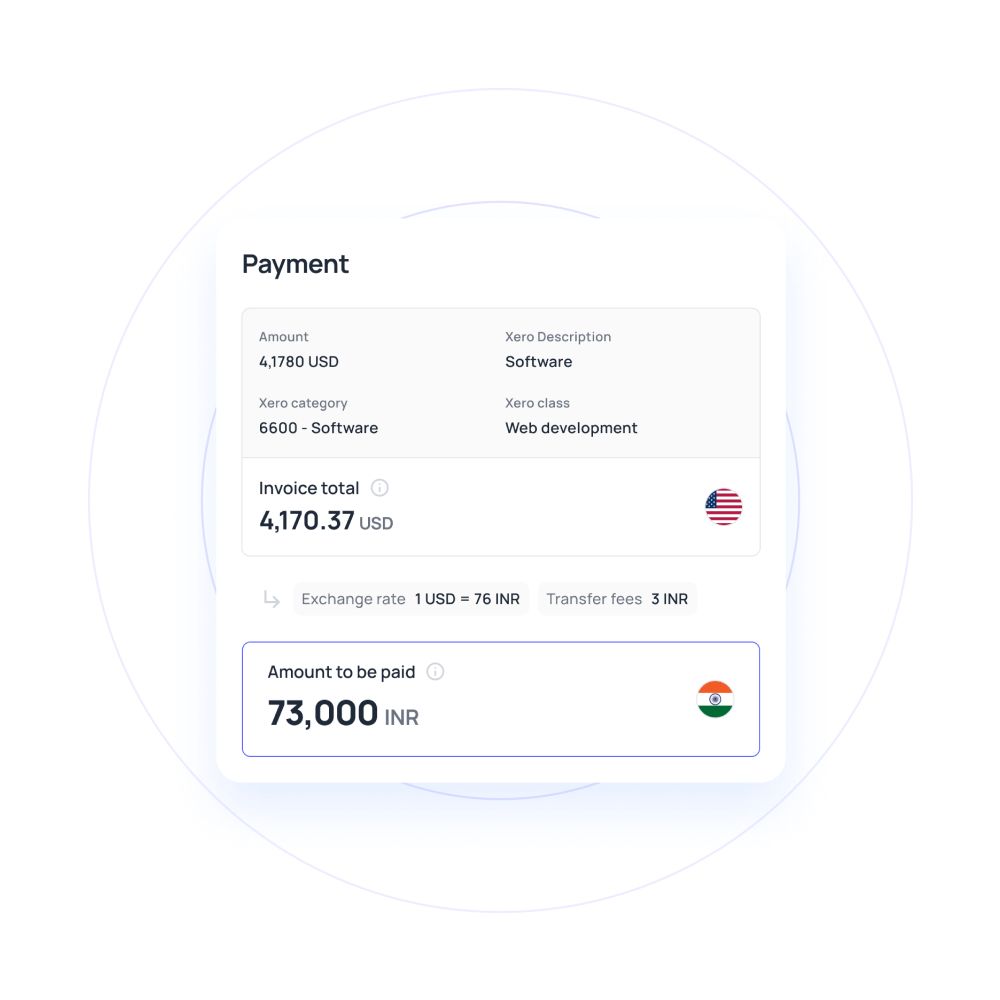
Differences between international money transfers and domestic money transfers
Money transfers are essential for businesses of all scales in today’s interconnected world. Whether transferring funds within a country or across borders, understanding the nuances between domestic and international money transfer is crucial.
This knowledge can influence decisions regarding costs, processing times, and regulatory compliance, ultimately affecting financial efficiency and strategy.
Currency conversion
One of the primary distinctions between international and domestic money transfers is currency conversion.
● Domestic transfers
Funds are moved within the same currency, eliminating the need for conversion.
● International transfers
Currency exchange is often required, introducing a layer of complexity. The exchange rate can fluctuate, impacting the amount received by the beneficiary.
Additionally, financial institutions or money transfer services may apply a markup on the exchange rate, increasing the cost of the transfer. This conversion process not only affects the transfer cost but also the predictability of the final amount received.
Regulatory framework
The regulatory environment for domestic and international money transfers varies significantly.
● Domestic transfers
Domestic transfers are typically governed by a single country’s regulations, which tend to be more straightforward and easier to navigate.
For instance, the regulations ensure that transfers comply with local financial laws and protect against fraud and money laundering.
● International transfers
In contrast, international transfers are subject to the regulatory frameworks of both the sending and receiving countries, as well as international financial regulations.
This can lead to increased scrutiny and more stringent compliance requirements, particularly with regards to anti-money laundering (AML) and combating the financing of terrorism (CFT) measures. The need to adhere to multiple sets of regulations can slow down the transfer process and add to the administrative burden for both individuals and businesses.
Processing time
The processing times for domestic and international money transfers can vary greatly.
● Domestic transfers
Domestic transfers are generally quicker, often completed within hours or by the following business day, particularly with systems like the ACH in the U.S. or SEPA in Europe, thanks to efficient national payment networks.
● International transfers
Conversely, an international money transfer tends to take longer because they involve multiple banks, various time zones, and additional procedures for currency conversion and regulatory compliance.
It is quite normal for international transfers to take a few days to finalize, contingent on the countries and transfer methods involved.
Transfer costs
Costs associated with money transfers can vary widely depending on whether the transfer is domestic or international.
● Domestic transfers
Domestic transfers generally have lower fees, as they don’t involve currency conversion or complex regulatory checks. In some cases, domestic transfers may even be free, especially within the same bank.
● International transfers
International transfers, however, can be costly. Fees may include currency conversion charges, transfer fees from the sending bank, and possibly additional fees from intermediary banks that facilitate the transfer.
These costs can add up, particularly for small transfers, where the fees might represent a significant portion of the transferred amount.
Intermediaries
Intermediaries play a different role in domestic and international money transfers.
● Domestic transfers
Domestic transfers typically involve fewer intermediaries, often just the sending and receiving banks. This direct connection simplifies the process and reduces costs and potential delays.
● International transfers
In contrast, international transfers often require multiple intermediaries, especially when the sending and receiving banks do not have a direct relationship.
These intermediaries, also known as correspondent banks, facilitate the transfer across different banking networks. Each intermediary involved may introduce additional costs and processing time, further complicating the transfer.
Use cases
The use cases for domestic and international money transfers differ based on their scope and purpose.
● Domestic transfers
Domestic transfers are often used for routine transactions, such as paying bills, transferring funds between accounts, or making local business payments.
These transfers are typically smaller in amount and more frequent.
● International transfers
International transfers, however, are often used for more significant transactions, such as paying for international trade, sending remittances, or making cross-border investments.
These transfers may involve larger sums and are less frequent, but they are crucial for global business operations and maintaining financial connections between countries.
Experience seamless and secure international money transfers
What are international money transfers used for in business?
In the globalized economy, international money transfers are vital for businesses operating across borders. These transfers enable companies to engage in international trade, manage overseas operations, and fulfill financial obligations.
Whether it’s paying for goods and services or repatriating profits, understanding the various uses of international money transfers in business is crucial for effective financial management.
Payment for goods/services
One of the most common reasons for which businesses send money internationally is the payment for goods and services.
Companies often source materials, products, or services from foreign suppliers. These transactions require the transfer of funds across borders, typically in different currencies.
International money transfers enable businesses to pay their suppliers in their local currency, which can be crucial for maintaining good relationships and securing favorable terms.
These payments are often made through bank transfers or specialized payment platforms that facilitate cross-border transactions.
Settling invoices and bills
International money transfers are vital for settling invoices and bills with overseas suppliers, service providers, and partners.
Globally operating businesses frequently handle invoices in various currencies, and prompt payment is crucial for sustaining good relationships and preventing late fees.
Whether it's for raw materials, marketing services, or technology licenses, international money transfers enable businesses to efficiently fulfill these financial commitments.
Typically, this process is facilitated through bank transfers or specialized invoicing platforms that accommodate multi-currency transactions.
Paying remote employees
As remote work has gained popularity, companies hiring individuals from different countries has become common practice.
Consequently, international money transfers are essential for compensating these employees in their local currencies.
This approach not only helps retain talent by ensuring timely and fair payment but also simplifies payroll processes for businesses.
Payment platforms and international payroll services are often used to manage these transactions, reducing the administrative burden on companies.
Funding overseas operations
Businesses operating in multiple countries rely on international money transfers to finance their overseas branches or subsidiaries.
These transfers are crucial for covering various expenses such as salaries, rent, utilities, and other operational costs.
Effective money transfer between the headquarters and international offices is essential for seamless operations across diverse financial landscapes.
These transfers enable companies to sustain their global footprint and guarantee sufficient funding for their foreign operations.
Settling debts
In the world of business, companies sometimes take on debt from foreign lenders or partners.
International money transfers are necessary for repaying these debts, whether they involve loans, credit lines, or other financial obligations.
Timely debt settlement is crucial for maintaining a good credit rating and preserving business relationships.
By efficiently managing these transfers, businesses can ensure they meet their financial commitments, avoiding potential legal issues or damage to their reputation.
Donations and sponsorships
Numerous companies participate in corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives, frequently including donations or sponsorships abroad.
International money transfers are essential for financing these efforts, whether they aid local communities, non-profit entities, or global events.
Through these transfers, companies can honor their CSR pledges, bolster their international reputation, and foster beneficial social transformations.
Such activities not only elevate the firm's standing but also fortify its relationships in vital markets.
Investment purposes
International money transfers are frequently utilized by businesses to make investments in overseas markets.
This can be through direct investments, acquisitions, or forming partnerships. Such investments might involve buying real estate, acquiring stakes in foreign enterprises, or establishing joint ventures.
These transfers enable businesses to broaden their investment portfolios and explore new markets.
Through these financial activities, companies can enlarge their international presence, attract new clientele, and potentially enhance their profits.
Repatriation of profits
For multinational corporations, repatriating profits from foreign subsidiaries back to the home country is a common practice.
International money transfers enable the smooth transfer of these profits, ensuring that the parent company benefits from the earnings generated by its overseas operations.
This process can be complex, involving tax regulations and exchange rates, but it is essential for maximizing business profitability.
Efficient repatriation of profits ensures that the company’s global earnings are effectively managed and reinvested as needed.
What information do you need for an international money transfer?
In the globalized economy, the ability to transfer money internationally is vital for businesses operating across borders. These transfers enable companies to engage in international trade, manage overseas operations, and fulfill financial obligations.
Whether it’s paying for goods and services or repatriating profits, understanding the various uses of international money transfers in business is crucial for effective financial management.
1. Recipient's details
The recipient's information is crucial for an international money transfer. You’ll need to provide the recipient's full name, address, and bank account number.
If the transfer is going through a bank, you’ll also need the recipient’s bank name, branch, and SWIFT/BIC code. These details ensure the money is directed to the correct account, reducing the risk of misdirected or unsuccessful transfers.
2. Sender's details
The sender’s details are equally important as those of the recipient. This includes the sender’s full name, address, and contact details. Depending on the transaction, the sender’s bank account information or identification may also be needed, especially for larger transfers.
Providing accurate sender details helps financial institutions verify the transfer’s legitimacy and maintain proper records for compliance.
3. Amount to transfer
You need to clearly specify the exact amount you wish to transfer, along with the currency in which the transfer will be made. This information is critical because any mistake here could result in the wrong amount being sent, leading to potential disputes or delays.
If the transfer involves currency conversion, it’s important to understand the exchange rate applied, as this will affect the final amount the recipient receives.
4. Purpose of transfer
The purpose of the transfer is often required by financial institutions, especially for international transactions, to comply with anti-money laundering (AML) regulations.
Common reasons might include payments for goods or services, remittances, or funding accounts abroad. Clearly stating the transfer’s purpose facilitates smooth processing and ensures compliance with relevant regulations.
5. Identification and verification
In accordance with regulations, it may be necessary for both the sender and the recipient to present identification and undergo a verification process. This process could involve showing a passport, driver's license, or other legitimate identification.
Additionally, businesses may be required to submit their registration documents. These measures are vital for preventing fraudulent activities during the business money transfer and ensuring compliance with global AML and anti-terrorism financing laws.
6. Payment method
The payment method refers to how the sender will fund the transfer. Common methods include bank transfers, credit or debit cards, and sometimes cash payments through money transfer services.
The chosen payment method can affect the transfer speed, costs, and convenience of the transaction. It’s important to choose a method that aligns with both the sender’s and recipient’s preferences and needs.
7. Fees and exchange rates
Understanding the exchange rates and associated fees is crucial for both the sender and the recipient. These fees may encompass intermediary bank charges, service fees from both the receiving and sending banks, and conversion charges for currency.
The exchange rates can greatly affect the sum received if the transaction involves currency conversion. Therefore, comparing these expenses among various providers is vital to secure the most economical transfer.
Streamline your international transfers with ease
Things to consider when transferring money internationally
Have an idea about the inter-bank rate
If you are choosing the traditional route of transferring money to another country through a bank, you should definitely first check what rates they charge for doing so. You should make sure to contact a bank representative and clarify the inter-bank rates as this fee is usually quite high and you’ll end up paying the receiver less than what they were actually supposed to get.
How secure it is
Most wire transfers online through banks or otherwise are quite safe as they must follow strict regulations in order to be in this business. The transfer networks ensure that they are adhering to country guidelines and carrying out each transaction in a secure way.
Speed of the money transfer
Most money transfer providers carry out international payments quite quickly. Some even in minutes. Usually, the transfers are completed between 1-5 days depending on the country you reside in, the country you are sending the money to, the currencies you’re dealing with, and other factors like national holidays, etc.
Look for the fee charges
Even if the rates a bank or service provider charges are not mentioned anywhere, it does not mean they don’t exist. You should ensure that you check what are the different exchange rate charges that each service provider is offering and which is the most feasible option for you.
Transfer limits and regulations
Providers and countries may have different limits on the amount you can transfer internationally per transaction or within a certain timeframe. These limits depend on the business money transfer method, the countries involved, and the provider's policies.
International transfers also fall under various regulations, such as anti-money laundering (AML) laws, which mandate compliance with identification and reporting requirements for both sender and recipient. Knowing these limits and regulations is vital to prevent transfer delays or rejections.
Cancellation and refund policies
It's critical to be acquainted with the cancellation and refund policies of your service provider before making an international transfer. Understanding the refund process can save time and reduce frustration if you need to cancel a transfer or if an issue arises.
While some providers offer a grace period for cancellations, others have more stringent policies. Being aware of these policies beforehand prepares you for any necessary transaction reversals.
Customer support & trackability
Reliable customer support is essential for international money transfers. Responsive customer service can greatly impact the resolution of any problems or delays.
Moreover, opting for a provider that offers tracking capabilities allows you to follow your transfer's progress in real time, offering reassurance and ensuring the funds are delivered as planned.
What are the different international payment systems?
International payment systems are vital for enabling secure and efficient cross-border transactions. They allow businesses and individuals to transfer funds with ease. The most commonly used systems include SWIFT, SEPA, ACH, CHAPS, TARGET2, and international wire transfers.
Each system offers distinct features, advantages, and constraints. A good understanding of these systems is beneficial in selecting the most suitable option for your international payment requirements.
1. SWIFT
Definition
The Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT) operates as a global messaging network that banks and financial institutions utilize to securely share information regarding financial transactions.
Founded in 1973, SWIFT has evolved into the fundamental infrastructure to send money internationally, linking over 11,000 entities across more than 200 countries.
Usage
The primary use of SWIFT is for conducting international bank-to-bank wire transfers. It offers a uniform format for relaying payment orders, which helps ensure transactions are carried out both accurately and securely.
When a bank commences a SWIFT transfer, it dispatches a message via the SWIFT network to the beneficiary's bank. This bank then processes the transaction and deposits the funds into the recipient's account.
Advantages
● Global reach
SWIFT is the leading international payment system, facilitating bank transactions across almost every nation.
● Security
SWIFT ensures the security of messages through encryption and secure transmission channels, safeguarding transaction data's confidentiality and integrity.
● Reliability
The standardized messaging format of SWIFT minimizes errors, guaranteeing precise interpretation and execution of payment instructions by all involved entities.
Drawbacks
● Cost
SWIFT transactions can incur high costs, with fees levied by both the sender's and receiver's banks. Transfer processes may also involve intermediary banks that impose their own charges.
● Speed
Despite its security, SWIFT is not the quickest method for international payments, with transfers potentially taking several days, particularly when several intermediary banks are part of the process.
● Complexity
The participation of numerous banks in a single transfer can introduce delays and complexities, notably when currency exchange or regulatory compliance issues arise.
2. SEPA
Definition
An initiative by the European Union (EU), the Single Euro Payments Area or SEPA has been designed to harmonize and simplify payments in euros across 36 participating countries.
SEPA allows for seamless cross-border euro transfers within the EU and several non-EU countries, making it easier for individuals and businesses to conduct transactions in a single currency.
Usage
SEPA is used for euro-denominated payments between accounts within the SEPA region. It includes three main payment schemes: SEPA Credit Transfer (SCT), SEPA Direct Debit (SDD), and SEPA Instant Credit Transfer (SCT Inst).
These schemes cover various types of transactions, from one-time payments to recurring direct debits and instant transfers. SEPA payments are commonly used for salary payments, bill payments, and business-to-business transactions within the Eurozone.
Advantages
● Low cost
SEPA payments are generally inexpensive, with most transactions either free or subject to low fees, especially when compared to traditional wire transfers.
● Speed
SEPA Credit Transfers typically take one business day to transfer money internationally, while SEPA Instant Credit Transfers are processed in real-time, providing immediate access to funds.
● Ease of use
SEPA payments are simple to initiate, requiring only basic information such as the recipient’s International Bank Account Number (IBAN) and the Bank Identifier Code (BIC).
● Harmonization
SEPA standardizes payment procedures across participating countries, making cross-border transactions as easy as domestic payments.
Drawbacks
● Limited scope
SEPA is limited to euro-denominated transactions within the SEPA region. It is not suitable for payments in other currencies or for transfers outside the participating countries.
● Currency restriction
SEPA is designed exclusively for euro transactions, which limits its usefulness for businesses and individuals dealing with multiple currencies.
● Bank dependency
The speed and efficiency of SEPA transfers depend on the participating banks, which can lead to inconsistencies in processing times.
3. ACH
Definition
ACH, or Automated Clearing House, is an electronic payment system utilized in the United States for processing debit and credit transactions in batches.
Overseen by the National Automated Clearing House Association (NACHA), it is commonly used for various domestic payments, such as payroll, tax refunds, bill payments, and direct deposits.
Usage
ACH is mainly utilized for domestic transactions within the United States. However, it can also be used to send money internationally via the ACH Global service, which allows U.S. businesses to send payments to recipients in certain countries.
ACH payments are frequently used for recurring transactions, including subscription services, mortgage payments, and government benefits.
Advantages
● Cost-effective
ACH transfers usually cost less than wire transfers, offering a budget-friendly choice for both businesses and individuals.
● Efficiency
ACH transactions are batch-processed, enabling efficient management of numerous payments, which is perfect for payroll and similar recurring transactions.
● Security
ACH payments are conducted over a secure network, minimizing fraud risk and protecting sensitive financial data.
● Convenience
ACH supports the straightforward automation of payments, providing ease for businesses that handle numerous recurring transactions.
Drawbacks
● Speed
ACH payments are not instantaneous. They typically take one to three business days to process, which may be slower than other payment methods, especially for urgent transactions.
● Limited international reach
While ACH Global extends the system’s reach to some international transactions, it is primarily designed for domestic use, limiting its effectiveness for cross-border payments.
● Batch processing
The batch processing nature of ACH means that payments are not processed in real time, which can lead to delays, especially if payments are initiated outside of normal business hours.
4. CHAPS
Definition
Working as a real-time gross settlement (RTGS) system, the Clearing House Automated Payment System (CHAPS) is utilized in the United Kingdom for time-sensitive, high-value payments.
Started in 1984, CHAPS is managed by the Bank of England and frequently facilitates large transactions such as interbank transfers, corporate payments, and property acquisitions.
Usage
CHAPS is primarily used within the UK for same-day, high-value transfers between banks. It ensures that payments are processed in real time, meaning that funds are transferred instantly and irrevocably once the payment instruction is received.
CHAPS is typically employed for transactions where speed and certainty of settlement are critical, such as large business payments, real estate transactions, and financial market settlements.
Advantages
● Speed
CHAPS transactions are processed in real-time, ensuring that funds are transferred almost instantly on the same day.
● Certainty
Payments made through CHAPS are final and irrevocable, providing assurance to both the sender and recipient that the funds have been transferred securely.
● High-value transactions
CHAPS is designed for high-value transfers, making it ideal for large corporate payments, real estate deals, and other significant transactions.
Drawbacks
● Cost
CHAPS is typically more expensive than other payment methods, with fees charged by both the sending and receiving banks.
● Limited usage
CHAPS is primarily used within the UK, limiting its applicability for international transactions.
● Accessibility
CHAPS is generally used for large payments, making it less suitable for smaller or everyday transactions.
5. TARGET2
Definition
TARGET2 is the Trans-European Automated Real-time Gross Settlement Express Transfer System, operated by the European Central Bank (ECB) and the national central banks of the Eurozone.
It is a pan-European RTGS system used for settling large-value payments in euros across the EU. TARGET2 processes transactions in real time, ensuring immediate settlement and providing liquidity to the financial markets.
Usage
TARGET2 is primarily used by banks and financial institutions for cross-border euro transactions within the European Union. It is designed for high-value and time-critical payments, such as interbank transfers, securities settlements, and large corporate payments.
TARGET2 is also used by central banks for monetary policy operations and by businesses for cross-border trade and investment transactions.
Advantages
● Real-time settlement
TARGET2 provides real-time settlement of transactions, ensuring that funds are transferred immediately and reducing the risk of settlement delays.
● Pan-European coverage
TARGET2 covers the entire Eurozone, making it an efficient system to transfer money internationally, within the EU.
● Central bank oversight
TARGET2 is operated by the ECB and national central banks, ensuring a high level of security, reliability, and regulatory compliance.
Drawbacks
● Complexity
TARGET2 is primarily designed for banks and large financial institutions, making it less accessible for smaller businesses or individuals.
● Cost
TARGET2 transactions can be expensive, especially for smaller payments, due to the fees charged by participating banks.
● Limited currency
TARGET2 only processes transactions in euros, limiting its usefulness for payments in other currencies.
6. International wire transfers
Definition
International wire transfers are electronic transfers of funds between banks in different countries. These transfers are facilitated by networks such as SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication) and involve the transfer of money from one bank account to another, across international borders.
Wire transfers are commonly used for both personal and business transactions, including payments for goods and services, remittances, and investments.
Usage
International wire transfers are widely used for cross-border payments of various sizes and purposes. They can be initiated through a bank or a money transfer service provider.
The sender provides the recipient’s bank details, including the bank name, account number, and SWIFT/BIC code, along with the amount to be transferred. The funds are then transmitted through the SWIFT network or other corresponding networks, eventually reaching the recipient’s bank account.
Advantages
● Global reach
An international money transfer made via wire can be sent to almost any country, making it a versatile option for cross-border payments.
● Security
Wire transfers are secure and traceable, providing assurance that the funds will reach the intended recipient.
● Wide applicability
Wire transfers can be used for a variety of purposes, including business payments, personal remittances, and investments.
Drawbacks
● Cost
International wire transfers can incur significant charges, including fees from the sending and receiving banks, along with any intermediary banks participating in the transfer.
● Processing time
Secure yet time-consuming, wire transfers may require several days to finalize, particularly when several intermediary banks are part of the process.
● Currency conversion
Transfers involving different currencies can lead to extra expenses for the sender, stemming from adverse exchange rates and currency conversion fees.
Related read: How do international wire transfers work for businesses?
Transfer money internationally with Volopay
How to transfer money internationally through your bank?
The two most common ways you can wire transfer internationally are using the online website of your bank or directly visiting your bank’s branch nearest to you and getting help with the process from an employee.
Online bank transfer
1. Locating the wire transfer page on your bank’s website
The first step to making an online wire transfer through your bank is to navigate and find the wire transfer option. Log in to the bank’s website and you will most probably find the section somewhere on the top bar or left column of the homepage.
If you can’t find it, then try searching ‘wire transfer’ + ‘the name of your bank’ on Google and the page should most likely show up. If it still does not, you should call the customer support of the bank and get their assistance.
2. Check your transfer limit
Once you find the page check what your international money transfer limit is. If it is not already set by the bank, you will get an option to do so. If you find that the amount you want to transfer is more than the limit that is pre-set by the bank, then you will have to contact the bank personally and request them to increase it if you can’t do it manually on the website.
Banks keep such limits to ensure that there is no fraudulent activity taking place. And to ensure further safety of the money transfer limit from your account, they might ask for further verification from you in the form of special codes like OTPs sent to your phone number or email.
3. Bank details
To carry out a SWIFT transaction you will need to provide the following details:
● The name and address of your bank
● The name, address, and account type of the person who will be receiving the money.
● Payer’s (your) bank account number also known as IBAN (international bank account number)
● And finally, the recipient’s BIC/SWIFT code.
4. Selecting the amount and currency exchange
Next, you must select the amount and the currency you want to transfer the money in. Usually, the currency that is set by default in the wire transfer form would be the currency of your country. You could leave it as it is or change it to the currency of the recipient’s country.
But make sure that whatever currency you are selecting the money for the receiver to receive is supported by their bank. Else if you send the money in the wrong currency, the transaction could be rejected.
5. Processing fees
Before you finalize the amount you’re sending, check the processing fee that your bank will charge you for the transfer. This is usually higher than the rates that other third-party providers charge. There might be instances where the receiving bank will also charge a fixed fee.
And as we spoke about the SWIFT network, remember that the transaction could pass between 2-3 banks who may also charge a fee. You should get an idea of how much this could be from a bank representative and then decide the final amount you are paying so the receiver doesn’t receive much less than what you actually intended to send.
6. Figure out the estimated time taken for the transfer
Finally, once you complete the payment through the wire transfer page, your bank should show you an estimated time it will take for your funds to be transferred to the recipient. This will let you keep track of the transfer whenever you log in to your bank account.
In-person bank transfer
1. Take all necessary bank documents with you
When you have decided that you need to go to your bank’s branch and get personal assistance from an employee, make sure you bring all necessary bank documents and details along with you.
These include
● Bank account details you want to transfer money from.
● The bank name and address of the recipient
● The payee’s address, name, and bank account type.
● IBAN or the recipient’s bank account number
● Recipient’s SWIFT ID or Bank Identifier Code
2. Amount and currency
To select the final amount you want to transfer, talk to the bank employee who is assisting you and take into consideration all the fees that will be levied on the wire transfer.
If the recipient is transacting internationally on a regular basis, they probably have a multi-currency bank account. But you should still discuss with the receiver and make sure the currency they want the money to be transferred in.
3. Transfer fee
Finally, before the bank transfers your money, clarify the fixed charge you must pay. This will be different for all banks and depend on factors such as the amount you’re transferring as well as the currency exchange rate.
Once you complete the payment, the bank employee will let you know the estimated time for the transfer to reach the recipient’s account.
Alternatives to traditional bank transfers for international money transfers
Numerous methods exist for carrying out a business money transfer internationally, each offering distinct features, advantages, and fees. Popular options include international payment platforms, foreign exchange brokers, and peer-to-peer (P2P) transfer services.
Familiarizing yourself with these alternatives can assist you in selecting the most suitable method for your requirements.
1. Through international payment platforms
Definition
International payment platforms are online services that facilitate the transfer of funds across borders. These platforms, such as PayPal, Wise (formerly TransferWise), and Revolut, allow users to send money to recipients in different countries, often with lower fees and faster processing times compared to traditional banks.
They operate by leveraging technology to streamline the process of currency exchange and fund transfers, making it more accessible and convenient for users.
Advantages
● Convenience
International payment platforms offer a user-friendly experience, allowing users to transfer money from the comfort of their home or office. Transactions can be initiated through websites or mobile apps, and recipients can often receive funds directly into their bank account or digital wallet.
● Speed
Many international payment platforms process transactions quickly, with some transfers being completed within minutes or hours, depending on the destination and payment method. This is especially beneficial for time-sensitive payments.
● Transparency
These platforms typically offer transparent fee structures and exchange rates, allowing users to see exactly how much they will pay and how much the recipient will receive before confirming the transaction.
Transfer fee
The fees for transferring money internationally differ based on the service provider, the sum being sent, and the recipient's country. These fees may be a fixed amount or a percentage of the transferred sum, and some services may include a slight markup on the currency exchange rate.
Typically, international payment platforms offer a more economical option than conventional bank transfers, particularly for transferring smaller sums.
2. Using foreign exchange brokers
Definition
Foreign exchange brokers are specialized services that facilitate currency exchange and international money transfers. These brokers offer competitive exchange rates and are often used by businesses and individuals who need to transfer large sums of money across borders.
They operate by buying and selling currencies in the foreign exchange market, allowing them to offer better rates than banks or payment platforms.
Advantages
● Competitive exchange rates
One of the biggest advantages of using foreign exchange brokers is their ability to offer more favorable exchange rates compared to banks and other financial institutions. This is particularly beneficial for large transfers, where even a small difference in the exchange rate can result in significant savings.
● Personalized service
Availing the services of foreign exchange brokers brings a certain level of personalized service. They provide assistance and expert advice to help users navigate the complexities of international money transfers. For businesses that handle large transactions in various currencies, this can be particularly beneficial.
● Flexibility
Flexibility is a key advantage offered by foreign exchange brokers, who provide a broad range of transfer options. These options often include forward contracts, spot contracts, and limit orders, which afford users greater control over the terms and timing of their transfers.
Transfer fee
The transaction fees levied by foreign exchange brokers differ but are typically competitive, particularly for substantial transactions. Some brokers impose a flat fee, whereas others might provide transfers without a fee, instead making a profit on the currency exchange rate.
When it comes to a large-value business money transfer, the cost savings on exchange rates can surpass any fees, rendering brokers an economical choice.
3. Peer to Peer (P2P) transfers
Definition
Peer-to-peer (P2P) transfer services are platforms that connect individuals who want to exchange currencies directly with each other.
P2P platforms, such as PayPal's Xoom, Revolut, and Wise, allow users to send money internationally by matching them with others looking to transfer money in the opposite direction. These services cut out traditional intermediaries like banks, often resulting in lower costs and faster transfers.
Advantages
● Reduced costs
Peer-to-peer (P2P) transfers usually incur lower fees than traditional methods by bypassing banks or other middlemen, offering a cost-effective alternative for those seeking to minimize transfer expenses.
● Immediate transfers
P2P services enable immediate transactions between individuals, shortening the duration for the recipient to receive funds, which is advantageous for time-sensitive transfers.
● Worldwide reach
Operating predominantly online, P2P platforms are available globally, providing the convenience for users to effortlessly send and receive money across various countries.
Transfer fee
P2P transfer fees are typically lower than those charged by banks and even some international payment platforms. Fees may be a flat rate or a small percentage of the transfer amount.
Additionally, P2P platforms often offer more competitive exchange rates, further reducing the overall cost of the transfer. However, fees can vary depending on the currency, amount, and payment method used.
Experience effortless international money transfers with Volopay
Advantages of using international money transfer
Faster payments
Compared to other methods of sending money abroad, international wire transfers are mostly completed within 1-2 days depending on the amount you are transferring, the service you are using and the currencies involved in the exchange.
Easy to use
Thanks to the internet, you can literally send money to any part of the world all at the comfort of your home. Online wire transfers are as simple as logging in to the website of your service provider or bank, filling in the necessary information, and executing the transfer.
More transparency on the currency details
Rather than physically going to a bank, talking to a representative, and being stuck with the rates the bank charges, transferring money online gives you the freedom and flexibility to choose how you want to send money cross-borders. You get to compare each service provider and choose the best suitable option for yourself.
Better support
Payment methods that involve the SWIFT network have very good traceability. The network provides tracking details that help you know exactly where your money is in the online transfer process.
More secure
When you send money internationally through banks and service providers, they use modern technology to ensure that all transactions taking place through their networks are safe and follow country policies and guidelines.
Effortless international money transfers with Volopay
Volopay has the tools that can significantly streamline the intricacies of the international business money transfer, providing businesses with a smooth and effective method for managing cross-border payments.
With a focus on reducing delays and increasing oversight, Volopay's platform delivers essential features that simplify worldwide transactions.
1. No delays on international transfers
Volopay’s international money transfer ensures the prompt processing of transfers, facilitating the rapid movement of funds across borders.
This efficiency is vital for the seamless continuation of operations, especially when managing urgent payments such as clearing invoices or compensating foreign suppliers. Utilizing cutting-edge technology and a strong network, Volopay expedites the transfer procedure, assuring timely arrival of your payments.
2. Real-time payment tracking
One of the standout features of Volopay is its real-time payment tracking. With this capability, you can monitor the status of your international transfers from initiation to completion.
This transparency not only provides peace of mind but also allows you to stay informed about the progress of your payments, reducing the risk of errors or discrepancies and ensuring that your funds arrive as planned.
3. Multi-level approval workflows
Volopay’s platform supports multi-level approval workflows, giving your business the flexibility to manage payments with precision and control.
With Volopay multi-level approval, you can set up customized approval processes based on your organizational structure, ensuring that all payments are reviewed and authorized by the appropriate parties before being executed. This added layer of control helps prevent unauthorized transactions and enhances financial oversight.
4. Manage all your vendors seamlessly
With Volopay, managing your vendors becomes a breeze. The platform allows you to organize and pay all your international vendors from a single dashboard.
This centralized approach simplifies the process of handling multiple suppliers, reducing administrative burdens and streamlining your payment operations. You can also maintain a clear record of all transactions, helping you stay on top of your vendor relationships.
5. Foreign currency account
Volopay business account offers the convenience of a multi-currency account, enabling the holding and management of funds in different currencies.
This is particularly beneficial for globally operating businesses, as it aids in reducing currency conversion expenses and protecting against exchange rate volatility. Utilizing a multi-currency account allows for payments to vendors or partners in their local currency, enhancing efficiency and minimizing financial risk.
Related pages
Remittances are the exchange of money using a transfer medium. Read to learn more about what is remittance and the types of remittances.
Customers send the remittance advice to the vendors to inform them that the invoice payment is completed. Learn to know more.
Explore remittance money transfer, including its process, types, fees, risks, and mitigation strategies. Read on to learn more.
Make international payments faster and easier with Volopay
FAQs
International money transfers generally take 1 to 5 business days to complete. The duration depends on the destination country, the currencies involved, the transfer method, and whether any intermediary banks are part of the process.
For a business money transfer, you'll need the recipient's bank details (account number, SWIFT/BIC code), the amount to transfer, the currency, your business's information, and the purpose of the transfer. Some transactions may also require documentation for verification.
To send money internationally safely, use a reputable payment platform or bank, ensure that all recipient details are accurate, and verify any security measures offered by the service, such as encryption and multi-factor authentication.
Exchange rates depend on the currencies that are being exchanged as well as on the service providers being used. Financial institutions usually add a margin to the interbank rate. To ensure you secure the most advantageous rate for your currency transfer it is recommended to compare rates from different providers.
Yes, most banks and payment platforms offer tracking options for international money transfers. You can follow the transfer’s progress in real-time via online banking or the provider’s app, ensuring you stay informed throughout the process.
If your transfer fails or is delayed, reach out to your service provider's customer support immediately. They can investigate the issue, update you on the status, and potentially initiate a trace or refund if needed.
Transfer limits are set by the service provider, the destination country, and local regulations. Some platforms have specific daily or monthly limits, while banks may impose their own caps. Always check the terms before starting a transfer.
Cancellation options depend on the provider. Some transfers can be stopped before they are fully processed, but once completed, most transfers cannot be reversed. Review the terms carefully and contact customer support right away if cancellation is needed.
Volopay makes international money transfers easier by providing real-time tracking, multi-currency accounts, seamless vendor management, and multi-level approval workflows, which help streamline the process, reduce delays, and ensure secure, transparent transactions.
Yes, many platforms, including Volopay, offer the option to schedule recurring international payments. This feature is particularly useful for businesses with regular cross-border obligations, such as paying overseas suppliers or employees, ensuring timely and automated payments.