What are prepaid expenses? A complete guide for businesses in the US
Prepaid expenses are payments you make in advance for goods or services your business will use in the future. Common examples include rent, insurance, and software subscriptions. These payments aren’t just routine costs, they’re part of keeping your financial records accurate and your budgeting on track.
This is especially true when handling prepaid expenses for small businesses, where every dollar must be carefully planned and tracked. Tools like prepaid cards make managing these costs easier by allowing you to allocate specific budgets, automate payments, and track usage in real time.
What are prepaid expenses?
Prepaid expenses are advance payments your business makes for goods or services that will be used in the future. Instead of counting these costs as expenses right away, you record them as assets because the benefit is yet to be realized. Over time, as you consume what you've paid for, like insurance coverage, software access, or office rent, the value is gradually shifted from the asset column to an actual expense.
This method is rooted in accrual accounting, which aims to match expenses with the periods they benefit. It gives you a clearer picture of your financial performance and helps avoid overstating or understating profits.
Prepaid cards can be a useful tool here. They let you fund recurring costs upfront, control spending limits, and maintain clean records.
Whether it's monthly subscriptions or annual insurance premiums, tracking your prepaid expenses properly helps you stay organized and compliant.
Why are prepaid expenses important for businesses?
Managing prepaid expenses the right way isn’t just about staying organized, it’s about keeping your financial strategy strong and your operations efficient. These upfront payments, when tracked and allocated properly, play a key role in accurate accounting, tax planning, budgeting, and even cost savings. Here's how:
1. Accurate financial reporting
When you record prepaid expenses correctly, your financial statements reflect reality, not just what's in your bank account. Under accrual accounting, expenses must match the period they benefit.
Understanding what are prepaid expenses and applying this principle properly ensures your reports don’t misstate profitability. This alignment helps you stay compliant with GAAP standards and gives stakeholders a more accurate view of your company’s performance.
2. Cash flow planning
Cash flow is the lifeblood of your business, and prepaid expenses can either help or hurt, depending on how you manage them. Paying in advance for services like insurance or SaaS platforms can create predictable cash outflows, making it easier to map out your financial runway. This predictability is a powerful tool for planning. You know when money will leave your account and when the benefit kicks in.
Prepaid cards give you even more control, set monthly reload limits, automate recurring payments, and avoid surprise charges. By tracking these prepayments closely, you can forecast future cash needs with more accuracy and avoid liquidity crunches. For growing businesses, managing prepaid expenses with foresight is key to long-term stability.
3. Tax deduction strategy
Prepaid expenses can also affect your tax liability. In general, you can’t deduct the full value of a prepaid expense until it’s “used” or realized, according to IRS guidelines. That means if you prepay for 12 months of insurance in December, only one month’s worth may be deductible that year. Properly tracking and amortizing prepaid expenses ensures you're not taking deductions too early or missing them altogether.
A solid strategy can reduce errors and support compliance during tax season. Using prepaid cards helps reinforce this by keeping a digital trail of exactly when and where the payments were made. With clean records and accurate timing, you can structure your deductions to your advantage while staying within IRS rules.
4. Budget forecasting
If you want to tighten your budgeting process, tracking prepaid expenses is a must. These upfront costs often cover essential services your business relies on, so knowing exactly when they’re due and how they’re spread over time helps you plan your monthly and quarterly budgets with confidence.
This is particularly useful when managing prepaid expenses for small businesses, where margins are thin and predictability is crucial. With prepaid cards, you gain even more visibility. You can group prepayments by department or vendor, set category-specific limits, and track spending in real time.
5. Vendor discounts
One major benefit of prepaid expenses is the potential to negotiate better terms with vendors. Suppliers often offer discounts to businesses willing to pay in advance, and those savings can add up over time. Prepaying shows commitment and reliability, which can give you leverage in contract negotiations. It also reduces the administrative hassle of monthly billing.
Using prepaid cards to make these payments adds another layer of value; you can issue vendor-specific cards, control the exact amount paid, and keep a record of every transaction. This setup not only helps you secure deals but also simplifies reconciliation and audit prep. When you manage such expenses with the right tools, you turn early payments into smart financial moves.
Common examples of prepaid expenses
Prepaid expenses can take many forms, depending on the nature of your business. These are payments made ahead of time for services that span multiple months or years. Below are five common examples you’re likely to encounter, each one offering opportunities to streamline cash flow and improve budgeting, especially when paired with prepaid card solutions.
Prepaid rent
If your business pays rent in advance say, quarterly or yearly that's a prepaid expense. Instead of logging the full amount as an immediate cost, you divide it over the time you’ll occupy space. This keeps your books accurate and aligns with accrual principles.
Prepaying rent using a prepaid card makes the process smoother. You can dedicate a card specifically for rent, set the exact limit, and ensure payments are made on time without risk of overspending.
It’s useful for businesses managing multiple locations or coworking spaces, where separate prepaid cards can simplify expense tracking.
Prepaid insurance
Insurance policies often require full payment up front for coverage over several months or a full year. This qualifies as a prepaid expense because the benefit is received over time. You don’t expense the total immediately, instead, you allocate it across the coverage period.
You can set strict spending limits, automate renewals, and track when and where each payment is made. It also keeps your insurance costs isolated from other transactions, simplifying bookkeeping.
For growing companies with multiple policies, prepaid cards help maintain clarity and prevent duplicate payments.
Prepaid subscriptions
From CRM platforms to project management tools, businesses often prepay for software on an annual basis to receive a discounted rate. These prepaid subscriptions fall under prepaid expenses, since you’re paying now for a service used later.
Assign specific cards to teams or tools, cap spending, and track renewals automatically. This avoids surprise charges from auto-renewals or unused software. If a subscription needs canceling, lock the card immediately.
For companies relying heavily on digital tools, prepaid cards offer a smarter way to manage subscription costs.
Prepaid utilities
In some regions or contracts, businesses have the option to prepay for utilities like electricity, internet, or water. Doing so offers budgeting advantages, especially if rates fluctuate. Prepaid utilities are recorded as assets and expensed over the period they cover.
Using prepaid cards adds control, you can automate payments, monitor usage patterns, and ensure no missed due dates. This setup is especially helpful for businesses operating in shared or temporary spaces.
You get predictable monthly costs, fewer billing headaches, and an efficient way to ensure utility payments don’t get lost among hundreds of other transactions.
Prepaid advertising
Advertising platforms like Google Ads, Meta, or LinkedIn let you fund accounts in advance. This makes prepaid advertising a common expense, especially for businesses running long-term campaigns. Instead of expensing the amount upfront, you allocate it as the campaign runs.
Prepaid cards are ideal for this, they let you limit ad spend by campaign or channel, avoiding overspend or accidental charges. They also simplify reporting by keeping ad costs separate from other business expenses.
If you're managing multiple ad campaigns across departments or clients, assigning prepaid cards makes budget tracking and billing cleaner and more transparent.
How to account for prepaid expenses
Record as an asset
When you first make a prepayment, the cost isn’t recorded as an expense right away. Instead, it’s classified as a current asset on your balance sheet under "prepaid expenses. This reflects that the payment has not yet provided its full benefit. For example, if you prepay six months of rent, the total amount is entered as a single asset.
As time passes and the service is used, you gradually reduce this asset. Prepaid cards can help you manage this process by allowing you to separate and identify each prepaid transaction.
They also keep prepaid expenses isolated from daily operational costs, thereby making your overall asset tracking more precise and easier to reconcile.
Amortize over time
After recording the prepaid expense as an asset, you need to amortize it gradually as the benefit is consumed. Amortization is the process of spreading the cost over the time period the expense covers. So if you’ve paid $1,200 upfront for 12 months of software, you’ll expense $100 each month.
This approach keeps your financial reports accurate and compliant with accrual accounting rules. Prepaid cards make this easier by giving you transaction timestamps, which help set up an amortization schedule.
Some accounting software tools can sync with your prepaid card provider to automate this process, ensuring that expenses are shifted to the right months without manual errors or guesswork.
Journal entries
To properly account for prepaid expenses, journal entries are required at two points. First, when the prepayment is made, you debit the “prepaid expenses” account (an asset) and credit the cash or card account used to pay.
Later, as the benefit is used, you debit the appropriate expense account (e.g., Rent Expense, Insurance Expense) and credit the prepaid expense asset. These entries reflect the gradual shift from asset to expense and ensure your books stay balanced.
When you use prepaid cards, each payment is clearly documented, making journal entry preparation easier and more accurate. This also provides a clear audit trail, which is especially helpful during reconciliations and compliance checks.
GAAP compliance
To stay aligned with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), it’s essential that you record prepaid expenses in the period they provide value, not when the payment is made. This is part of accrual accounting, where timing matters.
For example, if you prepay for 12 months of service, you shouldn’t expense the full amount in month one you need to spread it across the service period. Failing to do this can distort profit margins and mislead stakeholders.
Prepaid cards support GAAP compliance by helping you clearly track when payments occur and what they cover. With accurate records, it becomes easier to match expenses to the right periods, maintain transparency, and avoid issues during audits or financial reviews.
Software integration
Modern accounting software makes managing prepaid expenses much easier, especially when integrated with prepaid card systems. Platforms like QuickBooks, Xero, and NetSuite can sync directly with your prepaid card data, automatically categorizing transactions and applying amortization schedules.
This integration minimizes manual work and reduces the risk of data entry errors. You can generate real-time reports, set reminders for when to allocate costs, and maintain up-to-date ledgers with minimal effort.
With prepaid cards feeding data directly into your accounting system, you get better visibility and stronger internal controls. For businesses scaling their operations or juggling multiple vendors, this automation is not just convenient, it’s a critical tool for staying accurate and compliant.
Prepaid expenses vs. other expense types
Understanding how prepaid expenses differ from other types of business costs helps you manage your accounting more accurately. It also helps avoid confusion when reviewing financial reports or filing taxes. Here’s how prepaid expenses compare to other common expense categories:
Prepaid vs accrued expenses
Prepaid expenses and accrued expenses are opposites in terms of timing. Prepaid expenses are paid before the benefit is received, like rent paid for the next six months. Accrued expenses, on the other hand, are incurred before payment is made, such as unpaid wages at the end of a month.
While prepaid expenses sit on your balance sheet as assets, accrued expenses are listed as liabilities. Both play critical roles in accrual accounting. The key differences between prepaid and accrued expenses can be seen in how prepaid cards simplify prepaid expense tracking, but don’t apply to accrued expenses, which often require invoices or post-payment reconciliation based on services already rendered.
Prepaid vs deferred expenses
Prepaid and deferred expenses are often confused, but have different implications. Prepaid expenses usually refer to short-term advance payments, typically under a year, like a 12-month insurance policy. Deferred expenses, however, can be long-term and involve spreading out larger investments such as multi-year software licenses or consulting contracts.
Both are assets when first recorded, but deferred expenses may remain on the balance sheet longer. Prepaid cards are best suited for prepaid expenses because they handle regular, short-term payments efficiently. For deferred costs, especially those tied to capital projects, you may need more robust accounting tools and longer amortization schedules.
Prepaid vs regular expenses
Regular expenses are day-to-day costs like salaries, office supplies, or utilities that are paid and consumed in the same accounting period. You record them immediately as expenses. Prepaid expenses, however, are paid upfront but benefit multiple future periods, so they must be recorded as assets and amortized over time.
This distinction matters when organizing your financial statements. Using prepaid cards helps separate prepaid expenses from regular ones. For example, rent paid annually via a prepaid card can be logged as a prepaid expense, while team lunch paid by company card is logged as a regular operating cost.
Financial statement impact
Prepaid expenses show up on your balance sheet as current assets because the service or benefit hasn’t been fully used yet. As time passes and the value is consumed, the cost is gradually transferred to your income statement as an expense. This process helps match costs to the correct accounting periods, improving the accuracy of your financial reports.
Other expenses, like accrued or regular costs, appear as liabilities or direct expenses right away. By managing prepaid expenses with prepaid cards, you gain better control over this flow, helping ensure payments are tracked, categorized, and transitioned correctly between financial statements.
Card-based prepayments
One advantage of managing prepaid expenses with prepaid cards is the ability to control and track spending in real time. Instead of using checks or ACH transfers, prepaid cards let you fund specific vendors, set spending limits, and generate a clear record of the transaction. This is especially useful when prepaying for multiple services like rent, subscriptions, or vendor retainers.
It also helps reduce errors, avoid unauthorized charges, and simplify reconciliation. Compared to traditional payment methods, prepaid cards offer more transparency and automation, making them a smart tool for businesses looking to better manage and monitor their prepaid expenses.
Benefits of managing prepaid expenses effectively
Managing prepaid expenses with intention and structure gives your business a financial edge. Instead of letting advance payments get lost in general expenses, smart tracking and allocation help you stay organized, save money, and plan better. Here’s how strong prepaid expense management benefits your operations:
Enhanced financial accuracy
When you manage prepaid expenses properly, your financial reports become more reliable. Rather than showing large spikes in costs when payments are made, you spread those costs out evenly over the period they cover.
A clear understanding of what are prepaid expenses helps you apply this method correctly and maintain consistency in reporting. It also keeps you compliant with accounting standards.
Budget control
Prepaid expenses often involve large sums of money paid upfront, which can disrupt your budget if not properly tracked. Managing these payments with prepaid cards helps you maintain tighter control. You can cap spending amounts, restrict card use to specific vendors, and avoid accidental overspending.
This level of control is especially useful for recurring expenses like subscriptions or insurance, where auto-renewals can sneak up and skew your budget. By clearly isolating prepaid transactions from day-to-day operational costs, you gain a more accurate view of available cash. This helps teams make informed financial decisions without second-guessing whether funds have already been committed elsewhere.
Tax optimization
Prepaid expenses can impact how and when you claim deductions. The IRS typically allows deductions only when the expense is realized, not when the payment is made. That means timing matters. If you don’t track prepaid expenses carefully, you risk misreporting deductions or missing them altogether.
Having a system in place ensures that each portion of a prepaid expense is claimed in the right tax year. Prepaid cards make this process smoother by creating a clear audit trail. Each card transaction is timestamped and categorized, which simplifies the handoff to your accountant or tax advisor. This level of organization helps reduce errors and supports smarter tax planning overall.
Operational efficiency
Handling prepaid expenses manually, especially when they involve multiple vendors or time periods, can get messy fast. Missed amortization schedules, untracked payments, and messy records all slow down your team.
When it comes to prepaid expenses for small businesses, these inefficiencies can lead to missed savings or compliance risks. Prepaid cards streamline the process by automating how and when money is spent. You can issue vendor-specific cards, preload exact amounts, and even schedule payments in advance.
Supplier savings
Many suppliers reward early payment with better rates or bonus terms. By managing your prepaid expenses well, you can take advantage of these opportunities and reduce overall costs. Prepaid cards help you act quickly when a vendor offers a discount for upfront payment, you don’t need to go through approval bottlenecks or wait for wire transfers.
Instead, you preload a card and complete the transaction instantly. You also avoid late fees or service interruptions, which can result from missed or delayed payments. In short, prepaid expense management supported by prepaid cards not only helps you stay on track, it can also directly improve your bottom line through negotiated savings.
Challenges of managing prepaid expenses
Amortizing prepaid expenses over time can get complicated, especially when juggling multiple payments across departments or vendors. Forgetting to allocate a monthly portion or miscalculating the schedule can throw off your books and result in inaccurate reporting.
Manual spreadsheets increase the risk of human error. Prepaid cards help automate this process when integrated with accounting software, allowing you to match each transaction to a schedule and get reminders for expense allocations.
This setup reduces the chance of missing entries and keeping your financial records consistent and audit-ready month after month.
Making substantial upfront payments can strain your company’s cash flow, particularly if timing is not carefully managed. A significant insurance premium or an annual software subscription might deplete funds required for payroll or inventory.
Prepaid cards offer a solution with strict spending limits and scheduled fund allocation, ensuring resources aren’t overcommitted. These cards also provide a transparent overview of funds for future expenses, helping prevent liquidity shortfalls.
Intentionally managing prepaid expenses safeguards your short-term cash flow while capitalizing on long-term financial advantages.
One of the biggest risks in managing prepaid expenses is misrecording them, either by logging the full amount as an immediate expense or forgetting to track them as assets. These errors can lead to distorted profit margins and complicate financial reviews.
Prepaid cards reduce risk by generating clean, timestamped records for each transaction. This eliminates guesswork about when and how payment was made. Assigning prepaid cards to specific expense categories also minimizes chances of misclassification.
Better recordkeeping leads to better decisions and fewer surprises at the end of the quarter or fiscal year.
Prepaid expenses must follow strict accounting standards to comply with GAAP and IRS regulations. If you misreport or misclassify them, your business could face penalties, failed audits, or tax issues. Common missteps include claiming deductions too early or failing to properly amortize costs.
Prepaid cards offer built-in compliance advantages. Every payment has a clear audit trail, and many platforms integrate directly with accounting tools, helping you maintain proper documentation.
That kind of precision is essential for staying aligned with regulatory requirements and avoiding costly mistakes.
Prepaying without clear terms can backfire if a vendor changes their service, cancels unexpectedly, or disputes the amount. Without a strong agreement, you risk losing money or struggling to get a refund. Prepaid cards offer some protection here, you can cap the amount paid or assign one-time use cards to vendors.
This gives you leverage and control over each transaction. Before making a prepayment, it’s also important to carefully review all contracts closely and confirm the exact service timeline in detail.
Combining prepaid cards with clear vendor agreements helps you manage prepaid expenses with less risk and more confidence.
Best practices for managing prepaid expenses
To make the most of your prepaid expenses and avoid the common pitfalls, you need solid systems in place. From automation to vendor negotiation, here are five proven strategies that help businesses handle prepaid costs more effectively.
Leverage accounting software
Manual tracking of prepaid expenses is prone to error. Using accounting software like QuickBooks, Xero, or NetSuite can automate much of the heavy lifting. These tools let you create amortization schedules, set reminders, and track each payment’s usage across time.
When integrated with prepaid cards, you get even more value, transactions are logged automatically, categorized, and matched to specific vendors or departments. This not only improves accuracy but also cuts down on time spent reconciling your books.
With clean, centralized data, you can generate reports instantly and ensure that your prepaid expenses are reflected properly in your financial statements without chasing paper trails.
Set amortization schedules
Once a prepaid expense is recorded, it needs to be amortized over its benefit period. Without a clear schedule, you risk overstating profits or missing deductions. The best practice is to build automated amortization schedules that align with your payment terms - monthly, quarterly, or annually.
Prepaid cards make this easier by isolating each transaction, so you know exactly when a cost was incurred and how long it should be spread out. Many accounting platforms allow you to tie card payments directly to amortization entries, ensuring nothing slips through the cracks.
With a structured schedule, your financial statements remain accurate and fully compliant throughout the fiscal year, giving stakeholders confidence and ensuring smooth long-term financial planning.
Monitor cash flow
Prepaid expenses can create cash flow challenges if not planned for properly. Large upfront payments can limit your available working capital. To avoid this, set cash flow forecasts that account for expected prepayments, and review them regularly. Prepaid cards support this by giving you better control over disbursements.
You can schedule card reloads in sync with your budget, preventing overspending and preserving liquidity. Monitoring cash flow closely also helps you decide whether prepaying is the right choice for a given vendor - sometimes, smaller monthly payments are more cash-efficient than annual prepayments.
Either way, visibility into upcoming expenses helps you stay financially agile, make informed decisions, optimize cash flow, and adapt quickly to changing market conditions with greater confidence.
Review vendor terms
Before prepaying for any service, take the time to review the vendor’s terms carefully. Look for refund policies, cancellation clauses, and service guarantees. Make sure the timeline of service matches the period you’re paying for.
Prepaid cards give you added leverage here, you can cap the transaction amount or pause payments if the service isn’t delivered as promised. It’s also a good idea to negotiate discounts or added benefits in exchange for prepayment.
Many vendors are open to this, especially when paid upfront. Combining strong vendor agreements with prepaid cards gives you both protection and flexibility, reducing the risk of disputes or wasted funds.
Conduct audits
Regular internal audits are essential for making sure your prepaid expenses are being handled correctly. Review amortization schedules, validate that expenses are recognized in the right periods, and confirm that all prepaid transactions are backed by documentation.
Prepaid cards simplify this process by generating detailed records of every payment - who it went to, when it happened, and what it was for. Many platforms offer downloadable reports that align with your chart of accounts, making it easy to cross-check records.
Routine audits not only catch errors but also strengthen your internal controls. They ensure your financials are audit-ready and reinforce accountability across teams.
How prepaid cards enhance prepaid expense management
Managing prepaid expenses is much easier when you have the right tools, and prepaid cards are one of the most effective. They simplify tracking, add layers of control, and integrate easily with accounting systems. Here’s how prepaid cards elevate the way your business handles prepayments:
Budget control
Prepaid cards give you tighter control over how much is spent and where. You can load exact amounts, restrict usage to certain vendors, and prevent overspending with hard limits. This is especially useful for managing recurring prepaid expenses like subscriptions, insurance, or vendor retainers. Instead of risking charges that exceed your budget, you can ensure every dollar has a defined purpose.
If a service doesn’t need to be renewed, simply stop funding the card. This level of control makes prepaid cards ideal for budgeting across departments or projects. You’re not just managing expenses, you’re preventing surprises and making sure every prepaid cost aligns with your financial goals.
Real-time tracking
With traditional payment methods, it’s easy for prepaid expenses to get buried in spreadsheets or forgotten in bank statements. Prepaid cards offer real-time visibility into every transaction. Most platforms provide dashboards where you can track activity as it happens, filter by team, vendor, or date, and even get instant alerts. This transparency helps you catch duplicate charges, spot unusual activity, and reconcile your books faster.
You can also assign cards to individual employees or departments, making it easier to see exactly who spent what, and why. For businesses with tight financial oversight, real-time tracking turns prepaid expenses from a guessing game into a controlled, predictable process.
Security features
Security is a major concern when handling company funds, especially for prepayments. Prepaid cards come with built-in features that protect your business. You can require PINs, set daily or transaction limits, lock cards instantly if misuse is suspected, and approve or decline spending requests before money is used. These tools minimize the risk of fraud, unauthorized purchases, or misuse of company funds.
Compared to traditional corporate cards or bank transfers, prepaid cards provide more granular control. If a vendor agreement falls through or a service gets canceled, you can cut off the card immediately without having to reverse a payment or dispute a charge.
Simplified bookkeeping
One of the biggest headaches in finance is keeping prepaid expenses organized across accounting periods. Prepaid cards solve this by generating clean, categorized transaction records that can be exported directly into your accounting software. Many systems offer native integrations with tools like QuickBooks, Xero, or NetSuite, so transactions appear where they should, automatically.
This removes manual entry, reduces reconciliation time, and ensures prepaid expenses are allocated correctly over time. Whether you’re tracking advertising credits, insurance premiums, or vendor retainers, having each prepaid transaction tied to a card simplifies everything. Your finance team gets clean data, fewer mistakes, and a faster close each month.
Vendor payment flexibility
Prepaid cards provide a flexible solution for managing vendor payments, particularly when prepayment is necessary or preferred. Businesses can issue virtual or physical cards for either one-time transactions or ongoing engagements, offering vendors a secure and direct payment option without compromising the primary business account. For international vendors, prepaid cards operating on major networks like Visa often prove more efficient than wire transfers or checks.
They also facilitate timely payments, enabling businesses to capitalize on early payment discounts or prevent service disruptions. With card-level controls, each payment can be customized to align with the vendor's terms, streamlining the prepaid expense process while enhancing vendor relations.
Common use cases for prepaid expenses in businesses
Prepaid expenses aren’t limited to just rent or insurance, they’re a flexible tool that businesses can apply across departments and functions. When paired with prepaid cards, these use cases become easier to manage, track, and optimize. Here are five common scenarios where prepaid expenses play a key role:
1. Small business operations
For small businesses, controlling costs is everything. Prepaying for essentials like rent, cloud storage, or software licenses helps you lock in rates and avoid last-minute charges. If you’ve been asking what are prepaid expenses in the context of a lean operation, they’re a way to stabilize costs and avoid cash flow surprises.
When you use prepaid cards, you gain even more control, as you can assign specific cards for recurring expenses, prevent overspending, and streamline everyday bookkeeping processes.
2. Corporate insurance
Most insurance providers offer more favorable terms for annual payments compared to monthly payments, making prepaid insurance a strategic and common expense for businesses. Utilizing a prepaid card to cover these policies helps segregate the transaction, ensuring it is not mixed with daily operating costs. This approach also minimizes the risk of missed payments or late fees.
Finance teams can load the exact amount onto a dedicated card, maintain proper documentation for audits, and automate the amortization schedule. Whether insuring employees, property, or operations, managing corporate insurance through prepaid cards enhances efficiency and accountability.
3. Marketing campaigns
Advertising platforms like Google Ads and Meta often allow businesses to prepay and draw from a credit balance. This helps control ad spend and simplifies budgeting. Prepaid cards are especially effective in this context you can assign separate cards for each campaign or platform, set strict limits, and pause spending instantly if needed.
This prevents budget overruns and unauthorized charges while also keeping campaign data clean for reporting. Whether you're running digital ads, influencer partnerships, or event sponsorships, managing marketing spend through prepaid expenses gives you a better handle on ROI and reduces the risk of overspending.
4. Equipment leasing
Leasing equipment is a common business expense, especially for companies in tech, manufacturing, or logistics. Some vendors require upfront payments for multi-month or yearly agreements. These become prepaid expenses, and managing them properly is key for accurate budgeting and compliance.
Prepaid cards make it easier to track these payments, ensuring funds are used only for approved leases. By assigning vendor-specific cards and logging transactions in real time, you avoid confusion later during audits or budget reviews. Whether it's laptops, printers, or machinery, prepaid cards help keep equipment costs separate, scheduled, and fully accounted for.
5. Employee benefits
Businesses often prepay for employee-related services like training programs, wellness platforms, or benefit subscriptions. These are prepaid expenses that support workforce development and retention. Using prepaid cards to fund these initiatives adds control and clarity. You can allocate a fixed budget to HR or team leads, monitor usage, and restrict spending to specific vendors.
This prevents unapproved purchases and helps ensure benefits align with company goals. It also simplifies tracking for reimbursements and tax reporting. Whether it's prepaying for online courses or gym memberships, managing these expenses through prepaid cards supports transparency and smarter benefit planning.
Prepaid expenses and financial statements
Prepaid expenses don’t just affect how you manage cash, they also influence how your financials are structured and interpreted. Here's how these payments show up across different financial statements and what they mean for your reporting and performance.
Balance sheet effects
Since prepaid expenses are meant to represent economic benefits in the future, they are initially recorded as current assets on the balance sheet. For example, if you prepay $10,000 for a year-long insurance policy using a prepaid card, the entire amount appears under "Prepaid Expenses" in your assets.
With every passing month, as the insurance coverage is consumed, a portion of that asset is transferred to the income statement as an expense. Using prepaid cards helps ensure accurate and timestamped entries, making balance sheet management more precise.
Income statement impact
As prepaid expenses are amortized, they begin to appear on your income statement as operating expenses. This staggered recognition ensures that costs are matched with the time periods they benefit, in line with accrual accounting principles. If not managed properly, expenses may be recognized too early or too late, skewing profit margins and confusing stakeholders.
Prepaid cards can streamline this by allowing finance teams to link each payment with a specific amortization schedule. This ensures that monthly expenses are recognized consistently and accurately, improving the reliability of your profit and loss statement and avoiding major swings in reported earnings.
Cash flow statement
On your cash flow statement, prepaid expenses are reflected in the operating activities section as cash outflows. Since the payment is made upfront, it shows up immediately, even though the corresponding expense hasn’t yet hit your income statement. This can cause temporary mismatches between profitability and liquidity.
Tracking these payments with prepaid cards helps provide context. By reviewing transaction logs and categorizing prepayments separately, finance teams get a more complete picture of how cash is being used. Understanding this flow is key to managing short-term liquidity while still planning for long-term operational needs covered by those prepaid services.
Ratio analysis
Prepaid expenses can influence key financial ratios, particularly those that assess liquidity and efficiency. For example, high prepaid expenses may inflate current assets, temporarily improving your current ratio or quick ratio, even though the funds are no longer available as cash. If not tracked accurately, these metrics can give a misleading picture of financial health.
By using prepaid cards to handle and monitor prepayments, you ensure transparency in how those figures are calculated. Accurate classification and regular amortization help keep your ratios aligned with your actual financial standing, supporting better internal decision-making and more credible reporting to external stakeholders.
Investor perception
Investors and stakeholders look closely at how a company manages its finances, including prepaid expenses. If these costs are misclassified or inconsistently reported, it can raise questions about your internal controls and financial discipline. On the other hand, a well-documented, clearly structured approach to handling prepaid expenses demonstrates proactive financial management.
Prepaid cards support this narrative by offering audit-ready records, spending controls, and integration with accounting systems. When investors see that your prepaid costs are carefully tracked and aligned with long-term planning, it builds confidence in your leadership and your company’s ability to scale responsibly and sustainably.
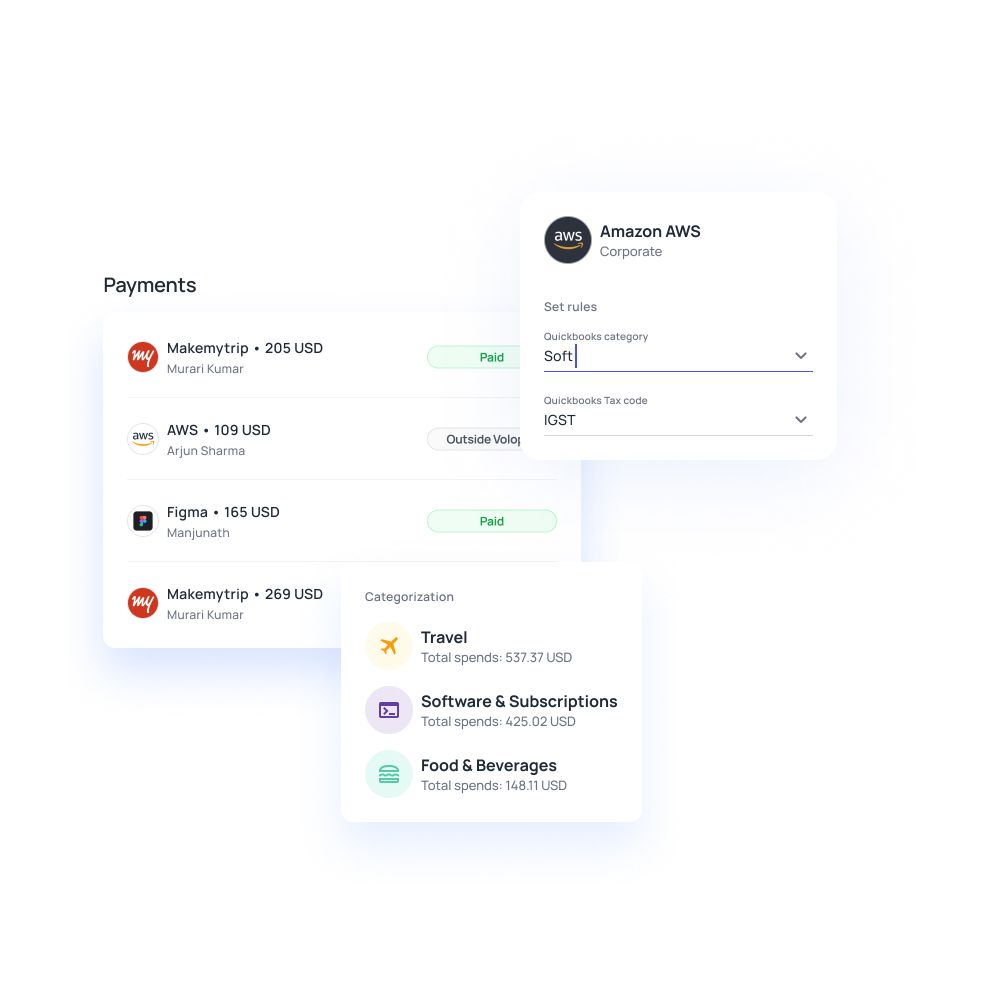
Manage prepaid expenses seamlessly with Volopay’s prepaid cards
Handling prepaid expenses doesn’t have to be a manual, error-prone process. With Volopay’s prepaid cards, you can simplify every aspect of managing these payments, from disbursement to reconciliation.
Our comprehensive expense management platform is built to give businesses like yours full control and real-time visibility over how prepaid funds are used, helping you stay organized, compliant, and financially efficient.
Budget control
Budget control is built into every card. You can assign cards to specific vendors, departments, or expense categories, and set custom spending limits for each. Whether you're prepaying for rent, subscriptions, or annual services, you never have to worry about going over budget. Funds are locked to the amount you choose, and unauthorized transactions are automatically blocked.
Real-time tracking
Monitor transactions via a dashboard, syncing with QuickBooks, Xero, or NetSuite for instant updates, ensuring accurate records, reducing manual effort, enhancing transparency, and supporting smarter, data-driven financial decisions every month.
Security
Security features add a layer of protection. Volopay cards can be locked, paused, or assigned for single use only. You can also implement multi-level approval workflows, ensuring that prepayments are reviewed and approved before the funds are released. This helps prevent misuse and builds accountability into every transaction.
Vendor flexibility
Vendor payment flexibility is another major benefit. Volopay’s prepaid cards are accepted globally, making them ideal for international vendors or remote service providers. You can make secure payments without needing wire transfers, and easily issue virtual cards for temporary or one-time use.
Compliance
Finally, Volopay supports compliance and audit-readiness. All transactions are automatically documented, and you can integrate your prepaid expense data directly with accounting platforms like QuickBooks, Xero, or NetSuite. This keeps your records organized, reduces the need for manual data entry, and makes audit preparation faster and stress-free.
Managing prepaid expenses doesn’t have to be complicated. With Volopay’s prepaid cards, you gain total control, real-time insight, and peace of mind, all in one system. Whether you’re a small business or scaling fast, Volopay helps you handle prepaid expenses the smart way.







Trusted by finance teams at startups to enterprises.
Bring Volopay to your business
Get started now
FAQs about prepaid expenses
Prepaid expenses are advance payments made by a business for goods or services that will be used in the future. These are recorded as assets on your balance sheet until the service or benefit is actually received, at which point they’re gradually expensed. In simple terms, if you’re trying to understand what are prepaid expenses, they are future benefits paid for today. Common examples include insurance, rent, and software subscriptions.
Prepaid cards make managing prepaid expenses easier and more efficient. You can assign cards to specific vendors or departments, set spending limits, and monitor transactions in real time. This helps prevent overspending and reduces the risk of unauthorized charges. By isolating prepaid payments from general business expenses, these cards also simplify reconciliation and improve financial accuracy. When integrated with accounting software, prepaid cards allow for automated tracking and reporting, making it much easier to manage amortization schedules and stay compliant with financial standards.
Prepaid expenses can impact when you claim deductions on your tax return. According to IRS rules, you generally can’t deduct the full value of a prepaid expense in the year it’s paid unless it meets certain criteria. Instead, you must deduct the cost over the period it provides value. This means accurate tracking and amortization are crucial. Prepaid cards help by providing clean documentation and timestamps, making it easier to ensure that expenses are recognized in the correct tax year and that your deductions are IRS-compliant.
Tracking prepaid expenses ensures your financial records are accurate, your budgets are realistic, and your tax reporting is compliant. Without proper tracking, you risk misstating profits, mismanaging cash flow, or missing out on eligible deductions. This is even more critical when handling prepaid expenses for small businesses, where limited resources demand precise financial oversight. Prepaid cards simplify the process by clearly separating prepayments from everyday spending, automating recordkeeping, and helping you stay on top of expense timing.
Prepaid expenses carry some risks, such as cash flow strain, vendor disputes, or misclassification in your books. If a vendor fails to deliver or a contract changes, your funds may be tied up. Poor tracking can also lead to compliance issues or tax errors. However, using prepaid cards helps reduce these risks by adding controls, visibility, and security to every transaction. With the right tools in place, prepaid expenses become less of a liability and more of a strategic financial decision for your business.